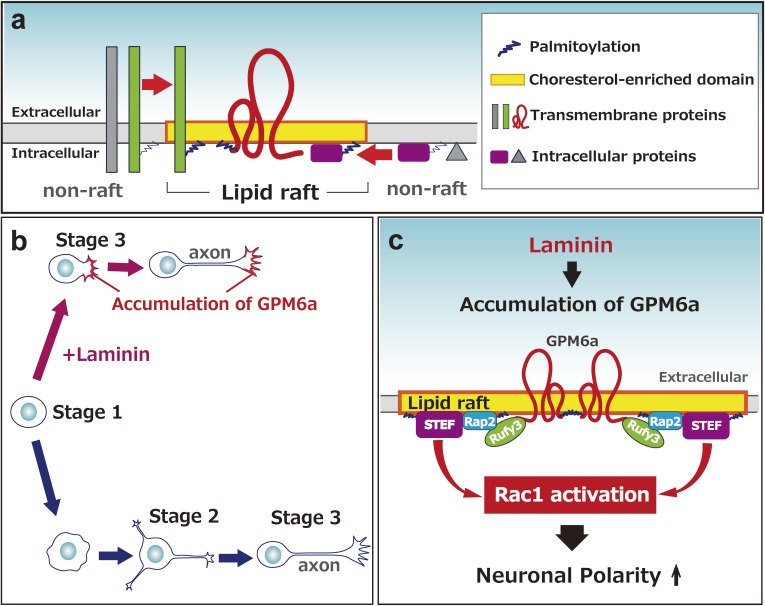
Figure 6.
Lipid rafts and palmitoylation are likely involved in neuronal development, especially in determining neuronal polarity and axon formation. (a) Lipid raft structure. Palmitoylated membrane proteins are translocated to lipid-raft domains from non-raft areas. (b) Polarity determination of neurons. Neurons are thought to have the potential for cell-autonomous polarity determination via stage 2 (multi-polar stage). However, LN- and GPM6a-dependent processes facilitate the polarity determination process by skipping stage 2 and directly moving to stage 3 (axon determination). (c) GPM6a-dependent signaling for polarity determination. Downstream proteins of GPM6a (Rufy3-Rap2-Tiam2/STEF) are gathered to lipid-raft domains in response to LN to facilitate signaling needed for neuronal polarity determination.