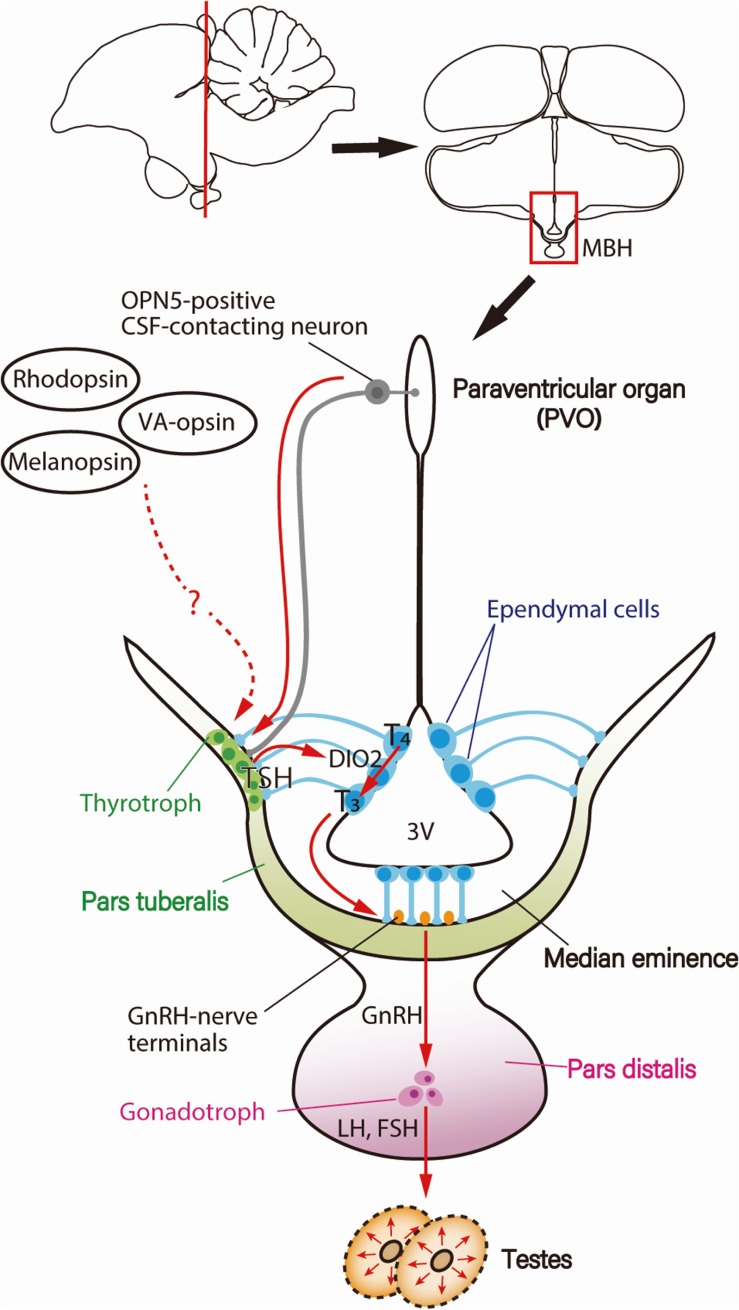
Figure 3.
(Color online) Photoperiodic signal transduction cascade for seasonal reproduction in birds. Light information received by deep brain photoreceptors, such as OPN5-positive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons, is transmitted to the pars tuberalis (PT) of the pituitary gland, inducing thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). PT-derived TSH then acts on the ependymal cells to induce a thyroid hormone-activating enzyme, type 2 deiodinase (DIO2), which converts the thyroid hormone precursor T4 into the active form T3. T3 regulates morphological changes in GnRH nerve terminals and glial processes, thereby facilitating GnRH secretion, resulting in the secretion of gonadotropin and gonadal development. Figure reproduced from Nakane and Yoshimura (2014)106) with permission under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) © 2014 Nakane and Yoshimura. Abbreviations: 3V, third ventricle; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; LH, luteinizing hormone; MBH, mediobasal hypothalamus.