Figure 3.
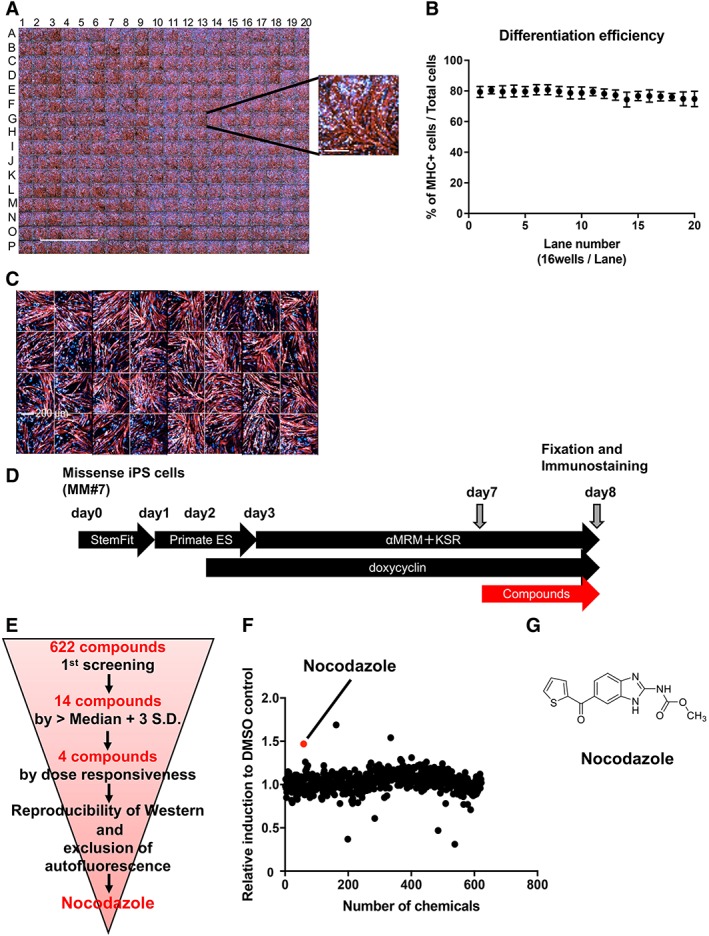
Construction of the Miyoshi myopathy (MM) myocytes (MM#7)‐based screening system and corresponding results. (A): Immunostaining of myosin heavy chain (MHC) in MM myocytes (MM#7) in a 384 multiwell plate on day 8. Scale bar: 5 mm. The inset on the right shows a high‐magnification image of a representative well (scale bar: 200 μm). (B): Mean differentiation efficiency of MM myocytes per lane (16 wells) in the same 384‐well plate described in panel (A). (C): Immunostaining of MHC in control myocytes (Control#17) plated in 32 wells of the 384‐well plate on day 8. Scale bar: 200 μm. (D): Schematic representation of the protocol for myocyte differentiation and small molecule screening. MM missense induced pluripotent stem cells were plated on a 384‐well plate on day 0 and cultured for 8 days. Small molecules were added on day 7. Cells were fixed on day 8, 24 hours after small molecule addition. (E): Schematic representation of the screening steps. Nocodazole was identified as the most effective molecule from the 622 compounds tested. (F): Result of the primary screen assay. Dot plot representation of the effects of 622 small molecules on dysferlin immunostaining relative to the dimethyl sulfoxide control; 3 μM and 0.3 μM of compounds (n = 1 each) were also evaluated (data not shown). (G): Structural formula of nocodazole.
