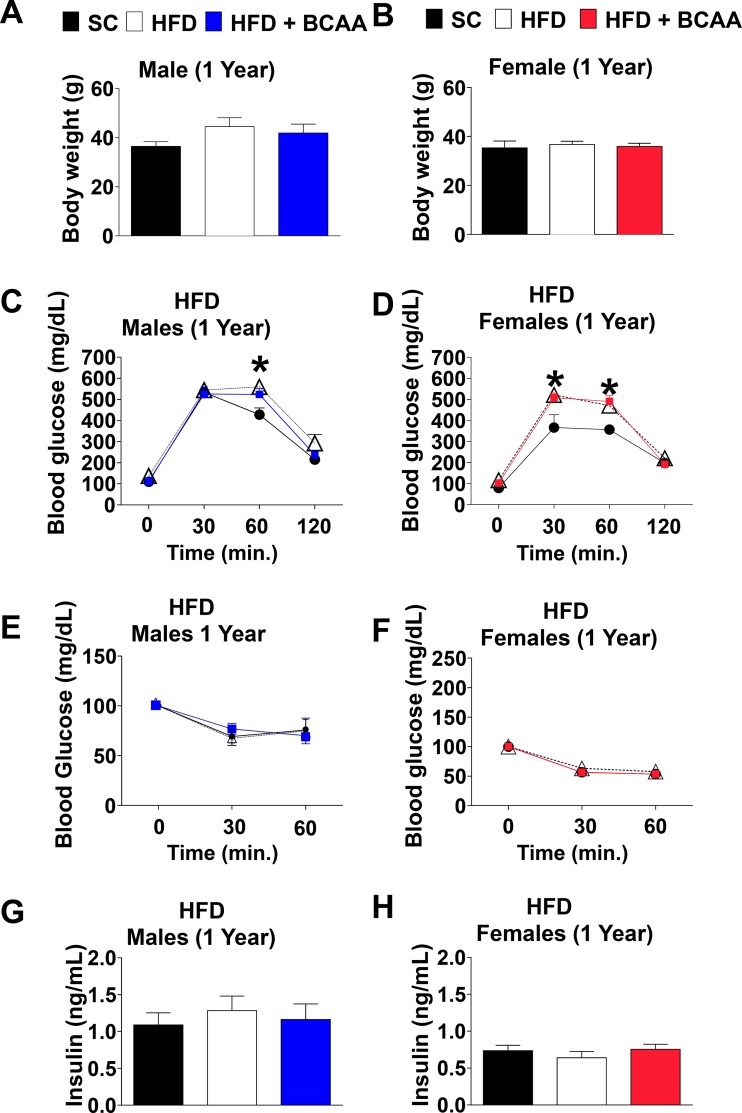
Fig. 2.
Aged offspring metabolic parameters challenged with high-fat diet (HFD). Body mass of 12-mo-old male (A) and female (B) offspring challenged with HFD for the period of 2 wk. Glucose tolerance tests (GTT) of 12-mo-old male (C) and female (D) offspring challenged with HFD for the period of 2 wk. Insulin tolerance tests (ITTs) of 12-mo-old male (E) and female (F) offspring challenged with HFD for the period of 2 wk. Fasted insulin levels of 12-mo-old male (G) and female (H) offspring challenged with HFD for the period of 2 wk. Data are presented as means ± SE; n = 6/group for males, and n = 6–8/group for females. *Significant effect (P < 0.05) of maternal diet [control diet vs. HFD or vs. HFD+ branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)], as assessed by one-way ANOVA with repeated measures for the glucose tolerance test (GTT) and ITT, followed by Newman-Keuls test.