Fig. 1.
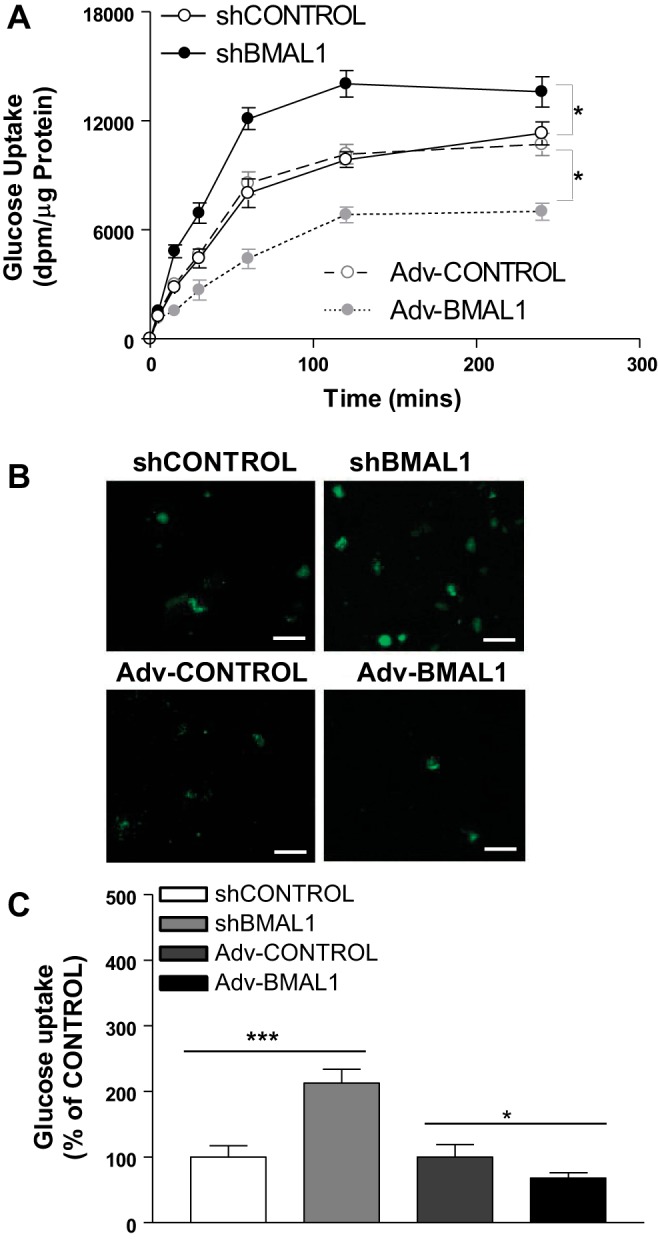
Effect of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein-1 (BMAL1) on glucose uptake. A: differentiated Caco-2 cells were transduced with control shRNA (shControl) [1.2 × 106 lentiviral transducing units (TU)/ml], BMAL1 shRNA (shBMAL1, 1.2 × 106 TU/ml), adenovirus (Adv)-Control (1.2 × 106 TU/ml), or Adv-BMAL1 (1.2 × 106 TU/ml) for 72 h. The accumulation and the transepithelial transport of [14C]methyl-α-d-[U-14C]glucopyranoside (1 µCi/ml) were determined at the indicated times. Each bar represents the mean ± SE of 3 separate trials. *P < 0.05, significantly different from shControl or Adv-Control, respectively. B and C: differentiated Caco-2 cells were transduced with shControl, shBMAL1, Adv-Control, or Adv-BMAL1 for 72 h and then treated with 2-NBD glucose (2-[N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)amino]-2-deoxyglucose) (25 mM) for 4 h, and then Caco-2 cells were photographed under a fluorescence confocal microscope. Scale bars: 100 µm (B). We then collected and measured the amount of 2-NBD glucose taken up by direct fluorometry (485/535 nM) using a plate reader; the amount of fluorometry was normalized with protein for each group (C). We repeated this experiment 3 times, and we calculated the mean of these 3 measurements. Each group represents the mean ± SE of 3 measurements. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, significantly different from each Control group.
