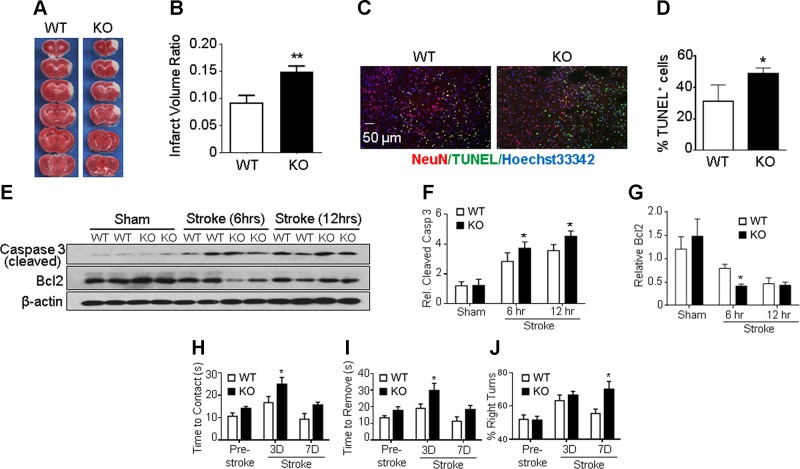
Figure 1.
GPR37 deficiency exacerbates brain injury, apoptotic cell death, and functional deficits after stroke. A) Infarct volume was measured 72 h after stroke using TTC staining on brain sections. Representative photographs of TTC staining of brain coronal sections from WT and GPR37 KO mice show a white-colored area corresponding to the ischemic core of the injured cortex. TTC staining at 24 h after stroke showed a similarly enlarged infarction in GPR37 KO mice (not shown). B) Quantification of infarct volume at 72 h based on TTC staining calculated using the indirect method. Damage to the brain was significantly larger in GPR37 KO mice than that in WT mice (unpaired Student’s t test; n = 17 and 18 in WT and GPR37 KO group, respectively). **P < 0.01. C) Cell death in the ischemic cortex was detected using TUNEL staining (green) in brain sections from WT and GPR37 KO mice. Red, NeuN staining of neuronal cells; blue, Hoechst 33342 staining of all cells. D) Quantified data of TUNEL staining 24 h after stroke. GPR37 deficiency significantly increased the number of dead cells after stroke (unpaired Student’s t test; n = 7 animals/group). *P < 0.05 vs. WT stroke controls. E) Representative Western blots with anti–caspase-3 and anti–Bcl-2 antibodies in the peri-infarct cortical tissue. F) Quantified results showing caspase-3 activation during subacute phases (6 and 12 h after stroke). This apoptotic event was significantly higher in GPR37 KO brains than in WT brains (2-way ANOVA; F = 97.97; n = 4/group). *P < 0.05. G) Expression of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 was significantly decreased in GPR37 KO mice after stroke compared with the WT control group (2-way ANOVA; F = 46.98; n = 4/group). *P < 0.05. H–J) Sensorimotor and locomotor functions were tested 3 and 7 d after stroke. The adhesive-removal test revealed that GPR37 KO mice needed prolonged time to contact (H) and remove (I) the sticky dot attached to their affected forepaws [2-way ANOVA; F (2, 53) = 10.34, F (2, 53) = 9.532, respectively] *P < 0.05. In the corner test (J), GPR37 deficiency significantly impaired whisker sensory function after stroke [2-way ANOVA; F (2, 44) = 5.316; n = 7 and 8/group].