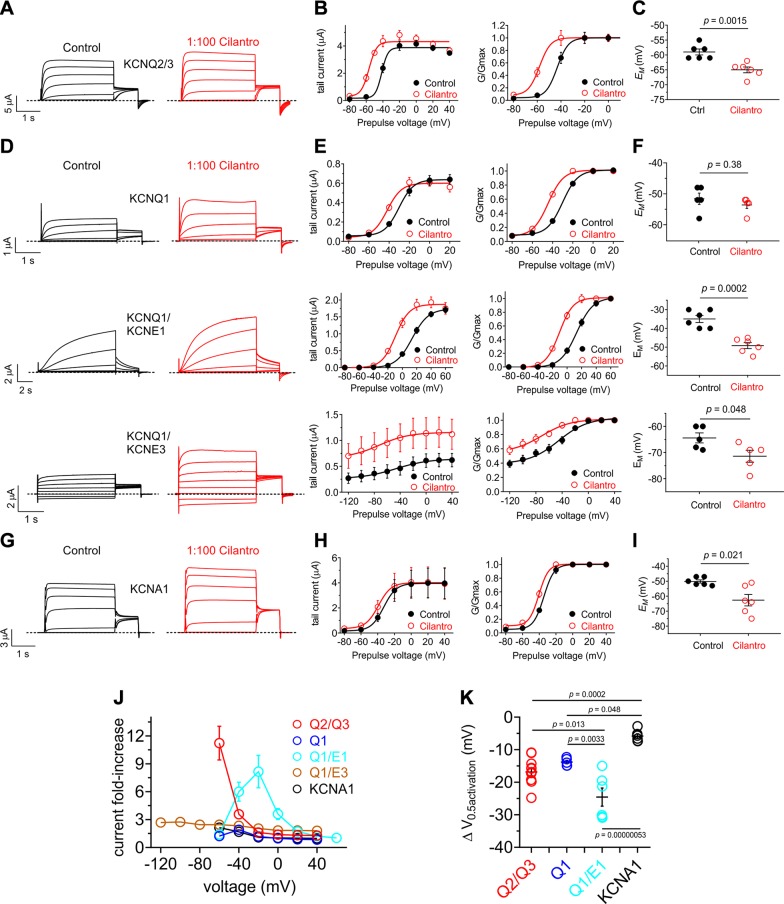
Figure 2.
Cilantro extract differentially activates heteromeric KCNQ channels All error bars indicate sem. A) Left, mean TEVC current traces for Xenopus oocytes expressing KCNQ2/3 in the absence (control) or presence of 1% cilantro extract (n = 6). B) Mean tail current (left) and normalized tail current (G/Gmax) (right) vs. prepulse voltage relationships for the KCNQ2/3 traces as in A (n = 6). C) Effects of 1% cilantro extract on EM of unclamped oocytes expressing KCNQ2/3 (n = 6). Statistical analysis by 2-way ANOVA. D) Left: mean TEVC current traces for Xenopus oocytes expressing homomeric KCNQ1 or heteromeric KCNQ1-KCNE channels as indicated in the absence (control) or presence of 1% cilantro extract (n = 5–6). E) Mean tail current (left) and normalized tail current (G/Gmax) (right) vs. prepulse voltage relationships for the traces as in D (n = 5–6). F) Effects of 1% cilantro extract on EM of unclamped oocytes expressing the channels indicated in D (n = 5–6). Statistical analysis by 2-way ANOVA. G) Left: mean TEVC current traces for Xenopus oocytes expressing homomeric KCNA1 in the absence (control) or presence of 1% cilantro extract (n = 6). H) Mean tail current (left) and normalized tail current (G/Gmax) (right) vs. prepulse voltage relationships for the traces as in G (n = 6). I) Effects of 1% cilantro extract on EM of unclamped oocytes expressing KCNA1 (n = 6). Statistical analysis by 2-way ANOVA. J) Current-fold increase vs. voltage for the Kv channel isoforms indicated, induced by 1% cilantro extract (n = 5–6). K) Scatter plot showing mean ΔV0.5 activation induced by 1% cilantro extract for the Kv channel isoforms indicated; n = 5–6. Statistical analysis by 2-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons.