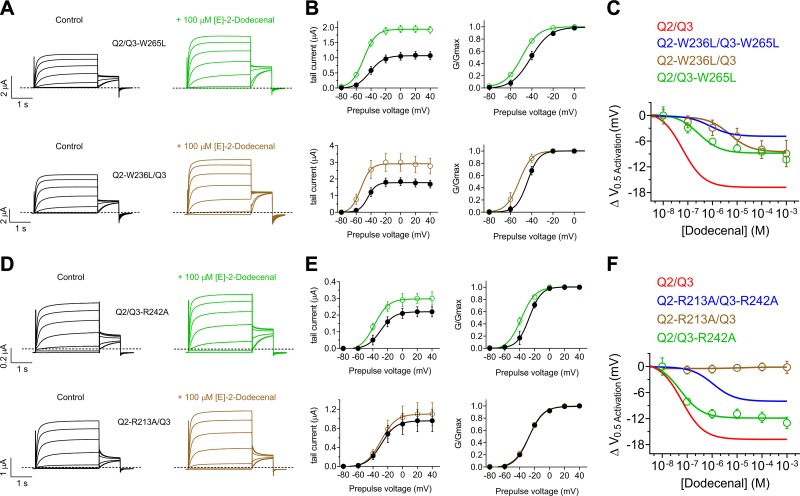
Figure 6.
KCNQ2-R213 is essential for KCNQ2/3 activation by (E)-2-dodecenal. All error bars indicate sem. A) Mean TEVC current traces showing effects of (E)-2-dodecenal (100 µM) on KCNQ2/KCNQ3-W265L (upper) and KCNQ2-W236L/KCNQ3 (lower) channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes (n = 5–6). B) Mean tail currents (left) and mean normalized tail currents (G/Gmax) (right) vs. prepulse voltage relationships for the traces as in A (n = 5–6). C) (E)-2-dodecenal dose response calculated from ΔV0.5 activation for wild-type, double-mutant (from Fig. 5), and single-mutant KCNQ2/3 channels as indicated; n = 5–6. D) Mean TEVC current traces showing effects of (E)-2-dodecenal (100 µM) on KCNQ2/KCNQ3-R242A (upper) and KCNQ2-R213A/KCNQ3 (lower) channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes (n = 5). E) Mean tail currents (left) and mean normalized tail currents (G/Gmax) (right) vs. prepulse voltage relationships for the traces as in D (n = 5). F) (E)-2-dodecenal dose response calculated from ΔV0.5 activation for wild-type, double-mutant (from Fig. 5), and single-mutant KCNQ2/3 channels as indicated (n = 5).