Figure 1.
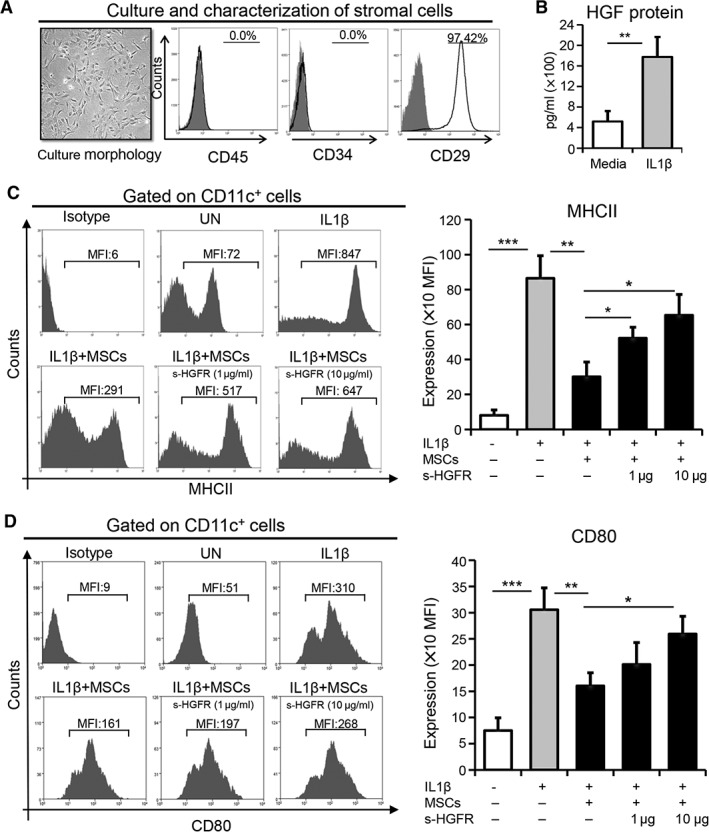
MSC‐derived HGF suppresses the maturation of antigen presenting cells. (A): MSCs were purified from bone marrow and expanded in vitro using MSC‐conditioned culture media via the plastic adherence method. Representative microscopic image exhibiting the morphology of expanded MSCs at passage two (left). Flow cytometry histograms showing negative expression of CD45 and CD34, as well as positive expression of CD29 (right). (B): Protein levels of HGF in the supernatants of MSCs cultured in media or stimulated with IL1β for 24 hours using enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay. Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and quantitative bar charts (right) demonstrating the expression of (C) MHCII and (D) CD80 on CD11c+ cells cocultured with MSCs in the presence or absence of IL1β (100 ng/ml) with or without s‐HGFR (1 or 10 μg/ml) for 24 hours. Each experiment was repeated three times. Data are represented as mean ± SD. t test: *, p < .05; **, p < .01; ***, p < .001. Abbreviations: HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; MSC, mesenchymal stromal cell; UN, untreated; s‐HGFR, soluble hepatocyte growth factor receptor; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
