Fig. 1.
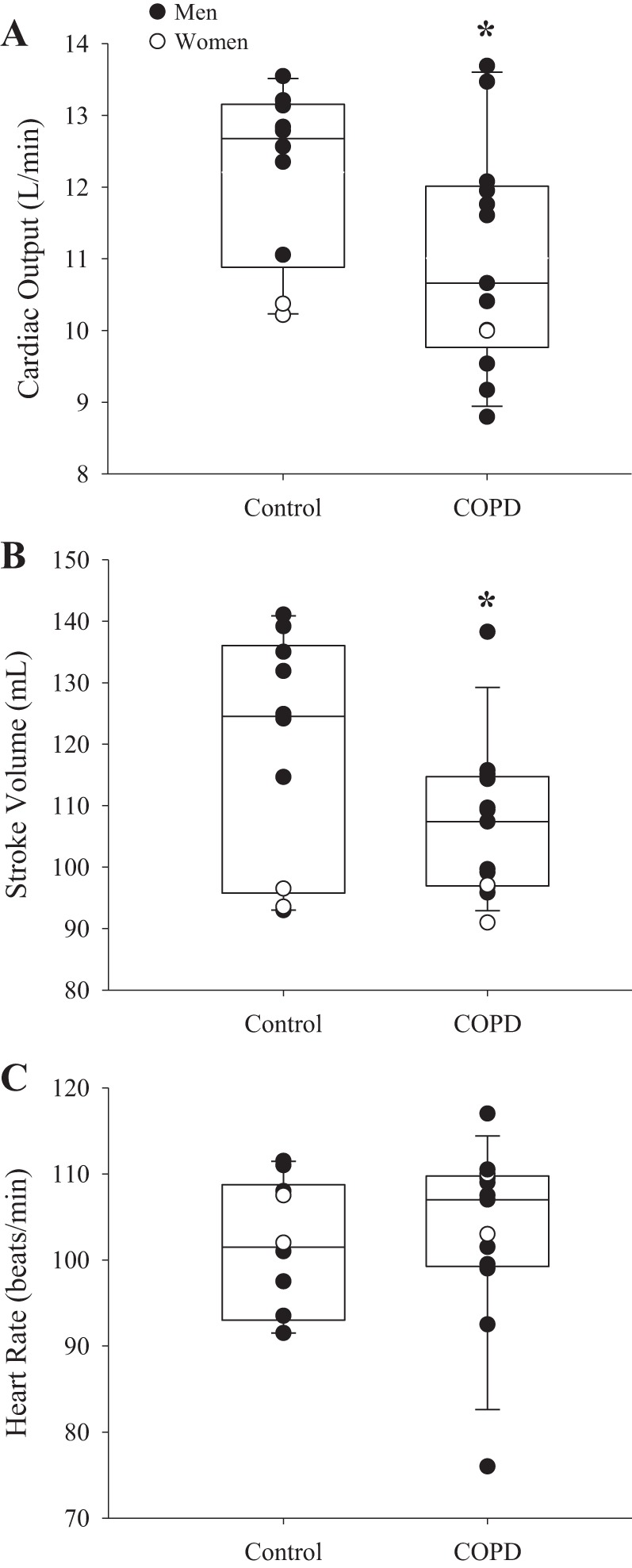
Central hemodynamics in controls and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Cardiac output (A), stroke volume (B), and heart rate (C) in controls (n = 10) and COPD patients (n = 13) during exercise. COPD had lower cardiac output and stroke volume than controls (both P < 0.04), whereas heart rate was not different between groups (P = 0.66). Data are reported as median and 25–75 percentile interquartile range. Significant differences were determined via unpaired t-tests. *Significantly different from control. Men and women are presented in closed and open circles, respectively.
