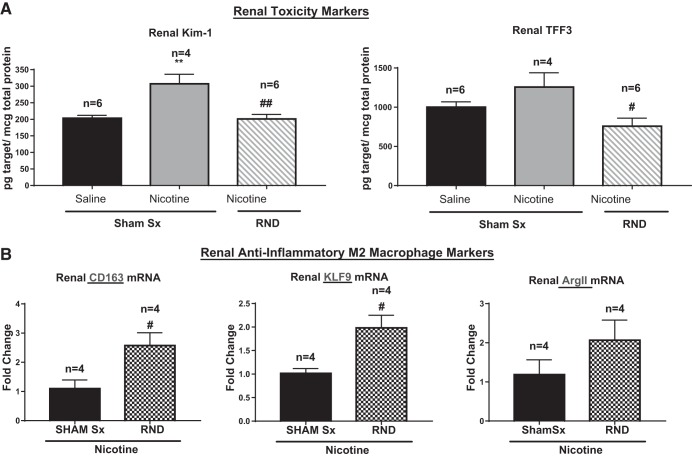
Fig. 4.
Renal nerve denervation (RND) decreases nicotine-induced renal toxicity and activates anti-inflammatory pathways. Renal tissue and serum were collected from young 3- to 4-wk-old spontaneously hypertensive rats that underwent sham surgery (Sham Sx) or bilateral RND, followed by subcutaneous infusion of nicotine (15 mg·kg−1·day−1) for 2 wk. Sample sizes as indicated. A: levels of renal toxicity markers [kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1) and trefoil factor 3 (TFF3)]. Levels of toxicity markers were assessed by Luminex assay. B: anti-inflammatory M2-macrophage markers CD163, KLF9, and arginase II (Arg II) were assessed by RT-PCR. Sample sizes: **P < 0.01, compared with Sham Sx treated with saline. #P < 0.05, and ##P < 0.01, compared with Sham Sx treated with nicotine. Groups were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test (A) and Student’s t-test between the RND + nicotine and Sham Sx + nicotine groups (B). Error bars represent means ± SD.