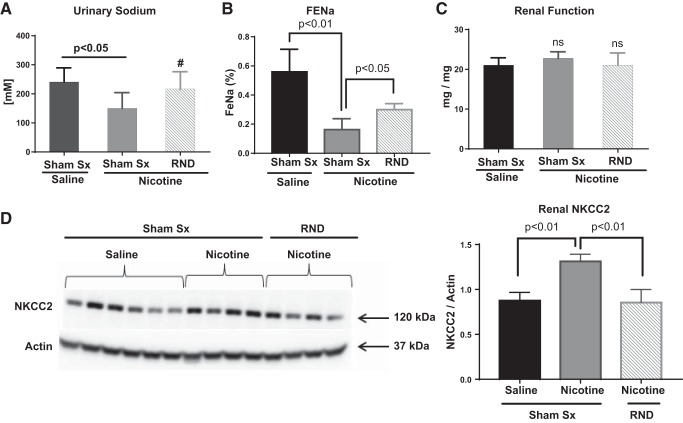
Fig. 6.
Renal nerve denervation (RND) decreases cholinergic-induced renal sodium retention and expression of sodium-potassium chloride cotransporter (NKCC2). Young 3- to 4-wk-old spontaneously hypertensive rat underwent either sham surgery (Sham Sx, n = 14) or bilateral RND (n = 16), followed by subcutaneous infusion of either saline (n = 12) or nicotine (15 mg·kg−1·day−1; n = 18) for 2 wk (similar to Fig. 1). Renal tissues and urine were collected at the end of infusion. A–D: spot urine sodium was determined by colorimetric assay (A), fractional excretion of sodium (FeNa) was calculated (B), urine protein to creatinine ratios were calculated as a measure of renal function (C), and renal homogenates (D) were assayed for the presence of sodium-potassium chloride cotransporter (NKCC2) by Western blot analysis. Error bars represent means ± SE. P values are as indicated based on Student’s t-test. #P = 0.16, compared with Sham Sx + nicotine, suggesting trend toward increase in spot urinary sodium.