Figure 6.
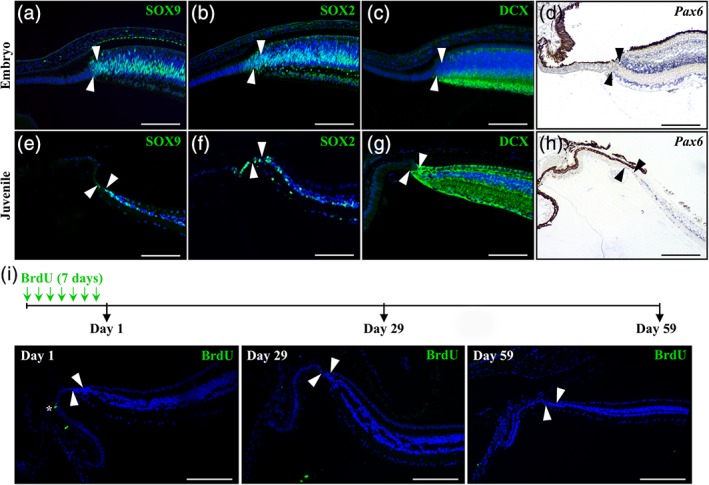
Expression pattern of retinal and proliferation markers in the peripheral retina of P. guttatus. (a–h) Immunohistochemistry (a–c, e–g) or in situ hybridization (d, h) showing the expression of various retinal stem cell (SOX2, SOX9, Pax6) or differentiation (DCX) markers at the peripheral dorsal retina in P. guttatus at both embryonic (12 dpo, a–c; 20 dpo, d) and juvenile (<1‐year old; e–h) stages. The names of retinal markers (color‐coded according to the immunofluorescence signal for protein detection) are shown on the top right corner in each panel. Only the retinal peripheral margin is delimited (solid arrowheads), as the RCJ is strongly reduced in snakes. (i) The top schematic drawing depicts the experimental strategy and BrdU pulse‐chase time points (black arrows). Retinal tissues were collected in newborn (<3‐months old) P. guttatus chased for 1, 29, or 59 days from the first week of BrdU feeding, and sections from the peripheral dorsal retina were processed for immunohistochemistry with BrdU (green). Solid arrowheads delimitate the retinal peripheral margin, and the white asterisk indicates one BrdU‐positive cell in the ciliary epithelium (Day 1, left panel). Cell nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 100 μm
