Figure 1.
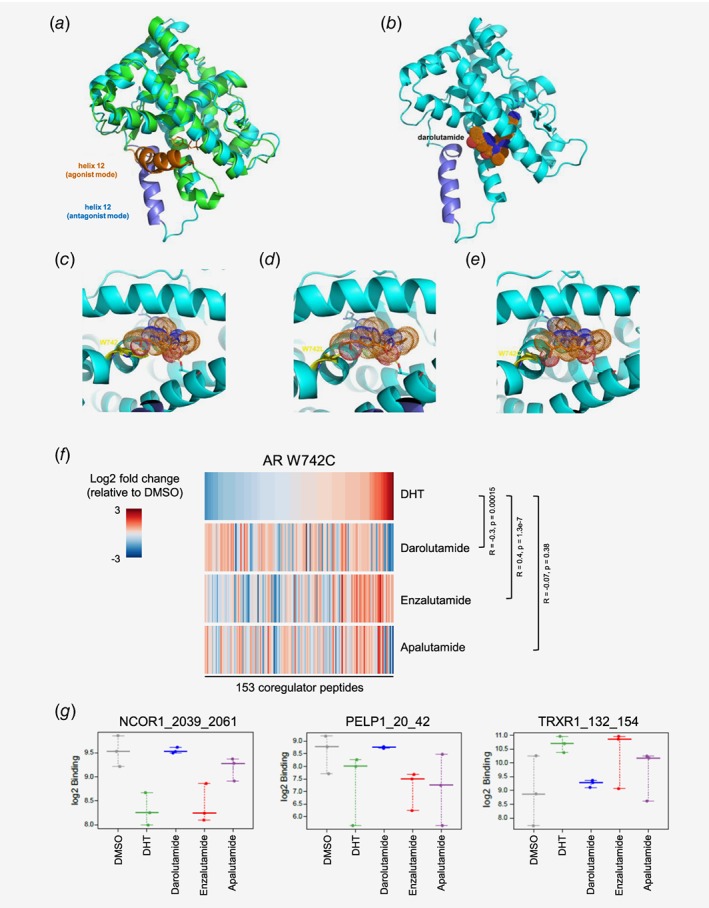
Visualization of antagonist binding to the AR LBD wild type or mutated at position W742, and impact on coregulator recruitment. (a) Superimposition of AR LBD crystal structure (pdb entry 4ojb, green) complex to bicalutamide (orange sticks) with helix 12 in agonistic conformation (orange) and structural model (cyan) with helix 12 in antagonistic mode (dark blue). (b) Darolutamide (dotted surface) modeled into the AR LBD in antagonist conformation. (c) Binding model of darolutamide (orange, sticks and dotted surface) suggests a stacking interaction of its pyrazole moiety to the indole of W742 (yellow sticks). (d) Binding model of darolutamide to AR W742L. (e) Binding model of darolutamide to AR W742C suggests formation of an H‐bond to the hydroxyethyl moiety. (f) Heatmap showing the overall pattern of coregulator peptide binding to the AR W742C after treatment with DHT or with different AR antagonists and sorted according to the effects observed after DHT treatment. Increased (red) and reduced (blue) recruitment are observed. (g) Examples of coregulator peptides for which a differential binding pattern for AR W742C was observed after treatment with different AR antagonists. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
