Figure 2.
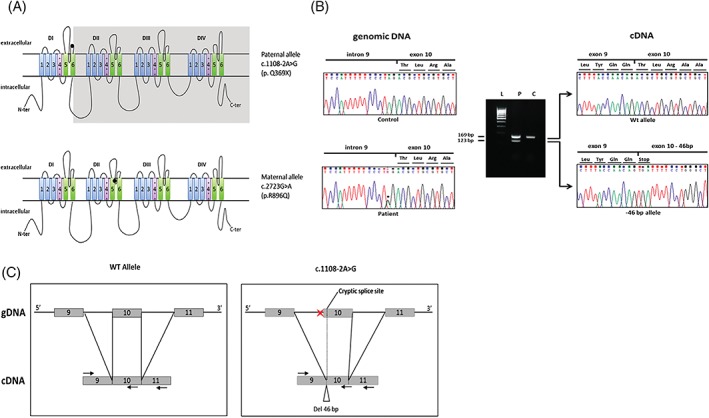
A, Localization of the two null mutations in Nav1.7 structure. The splicing mutation c1108‐2A>G on the paternal allele induces the premature truncation from the sixth segment of the first domain (S6‐DI). The missense mutation on the maternal allele is localized in the pore‐delimiting region. B, Proband SCN9A genomic sequencing, on the left side, revealed a nucleotide substitution in position c.1108‐2. The run on agarose gel show different bands from the SCN9A transcript amplification: in the patient lane (P) there is an unexpected fragment compared to the healthy control (C). Sanger sequencing of the two bands, on the right side, revealed the deletion of 46 nucleotides as a consequence of the canonical splicing site abolition and the new splicing‐acceptor site recognition. C, The splicing mutation on the genomic DNA and cDNA led to the deletion of 46 nucleotides on the mature transcript. Black arrows indicate the primer pair used for the cDNA amplification and sequencing
