Figure 3.
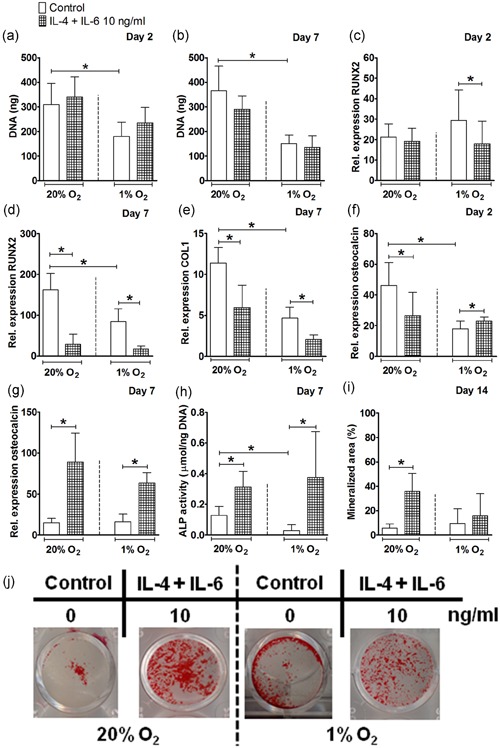
Effect of IL‐4 in combination with IL‐6 on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of hASCs under normoxia or hypoxia. (a,b) Hypoxia decreased DNA content in hASCs cultured without the combination of IL‐4 with IL‐6 at Day 2 and 7. (c) The combination of cytokines decreased RUNX2 expression under hypoxia at Day 2. (d) At Day 7, hypoxia decreased RUNX2 expression. IL‐4 with IL‐6 decreased RUNX2 expression under normoxia and hypoxia. (e) At Day 7, hypoxia decreased COL1 expression. IL‐4 with IL‐6 decreased COL1 expression under normoxia and hypoxia. (f) At Day 2, hypoxia decreased osteocalcin expression. IL‐4 with IL‐6 decreased osteocalcin expression under normoxia and hypoxia. (g) IL‐4 with IL‐6 enhanced osteocalcin expression under normoxia and hypoxia at Day 7. (h) At Day 7, hypoxia decreased ALP activity. IL‐4 in combination with IL‐6 increased ALP activity under normoxia and hypoxia. (i) hASCs stimulated with IL‐4 in combination with IL‐6 showed increased mineralization under normoxia at Day 14. (j) IL‐4 with IL‐6 induced mineralization of hASCs under normoxia and hypoxia at Day 14. Results are mean ± SD from n = 3 (triplicate wells of three independent experiments). *Significant effect of IL‐4 in combination with IL‐6 under normoxia or hypoxia, p < 0.05. ALP: alkaline phosphatase; COL1: collagen type 1; hASC: human adipose stem cell; IL: interleukin; RUNX2: runt‐related transcription factor 2 [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
