Figure 1.
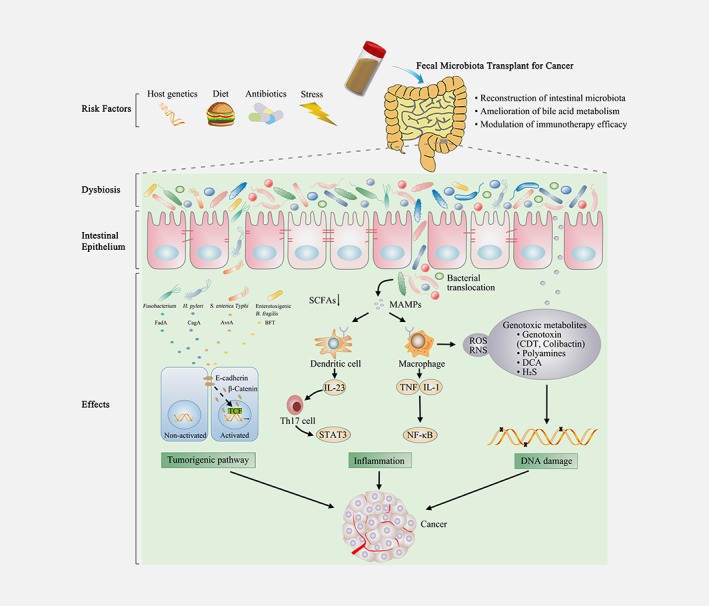
Management of cancer by fecal microbiota transplant. FMT represents a potential therapeutic strategy for cancer by reconstruction of intestinal microbiota, amelioration of bile acid metabolism and modulation of immunotherapy efficacy. Various factors such as host genetics, diet, antibiotics and stress could lead to alterations of gut microbiota, named as gut dysbiosis. Microbial dysbiosis and special bacteria in the gut are capable of affecting cancer development and progression via activating tumorigenic pathway, inducing inflammation and damaging host DNA. Special bacterial products, such as FadA toxin from Fusobacterium nucleatum, CagA protein from Helicobacter pylori, AvrA protein from S. enterica Typhi, and BFT from Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis can promote the separation of β‐catenin from E‐cadherin, which can trigger β‐catenin activation and contribute to tumorigenesis. The beneficial component in bacterial metabolites, such as SCFAs, is also decreased in microbial dysbiosis. Intestinal dysbiosis may be conducive to bacterial translocation, exerting pro‐inflammatory effects, which is mediated by MAMPs that activate TLRs in macrophages and dendritic cells. TLR signaling promotes the expression of the pro‐inflammatory factors, including IL‐23, TNF and IL‐1, thereby promoting carcinogenesis. Several microbial metabolites can directly or indirectly damage host DNA, fueling carcinogenesis. Special microbial toxins (CDT and colibactin) could directly induce DNA damage. Furthermore, gut bacteria also damage DNA indirectly via polyamines, DCA, ROS, RNS and H2S. FMT, fecal microbiota transplantation; BFT, Bacteroides fragilis toxin; SCFAs, short‐chain fatty acids; MAMP, microbe‐associated molecular pattern; TLR, Toll‐like receptor; IL‐23, interleukin 23; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL‐1, interleukin; Th17, T helper 17; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; NF‐κB, nuclear factor‐κB; CDT, cytolethal distending toxins; DCA, deoxycholic acid; H2S, hydrogen sulphide; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
