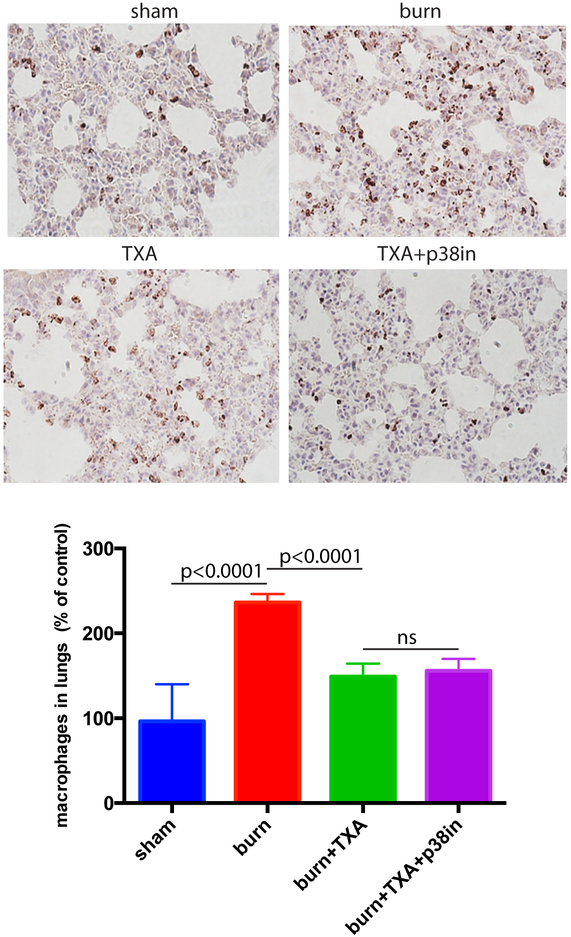
Figure 4. TXA inhibitor suppresses the burn-induced increase of macrophage presence in mouse lungs.
Mice received intraperitoneal injection of TXA immediately after undergoing burning procedure. A group of mice received both TXA injection and the topical p38 MAPK inhibitor. Mouse lungs were formalin fixed, paraffin sectioned, and stained for macrophage marker Mac1 (brown). The abundance of macrophages per tissue section area was calculated using Image J program. Mean and SD of macrophage abundance are shown. The mean of the control (sham) group was taken as a reference (100%) and used to divide all the means by. The statistical significance of differences between sham (N=4) and burn (N=4), burn and burn + TXA (N=4), and burn + TXA and burn + TXA + p38 MAPK inhibitor (N=4) groups was determined using t-test with Welch correction. Representative micrographs are displayed.