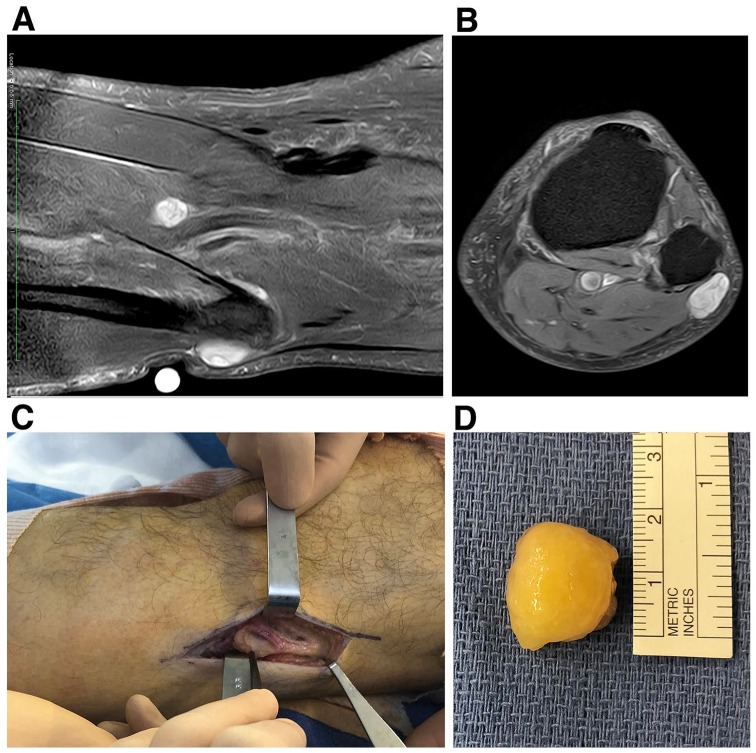
Figure 3.
Preoperative MRI evaluation (a,b) and intraoperative view (c,d) of the left-knee nodule. Two well-circumscribed lesions involving the common fibular nerve and the tibial nerve, respectively, were identified (a,b). While they both exhibited an heterogenous T2 hypersignal, they showed a weak and strong gadolinium-mediated enhancement (not shown), respectively. The common fibular nerve schwannoma was larger (24 × 14 mm) than the tibial nerve one (15 × 9 mm) and was readily enucleated without any neural damage (c,d). The common fibular nerve was carefully handled and its upper part with its lateral sural cutaneous branch was surgery free (c).
MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.