Figure 1.
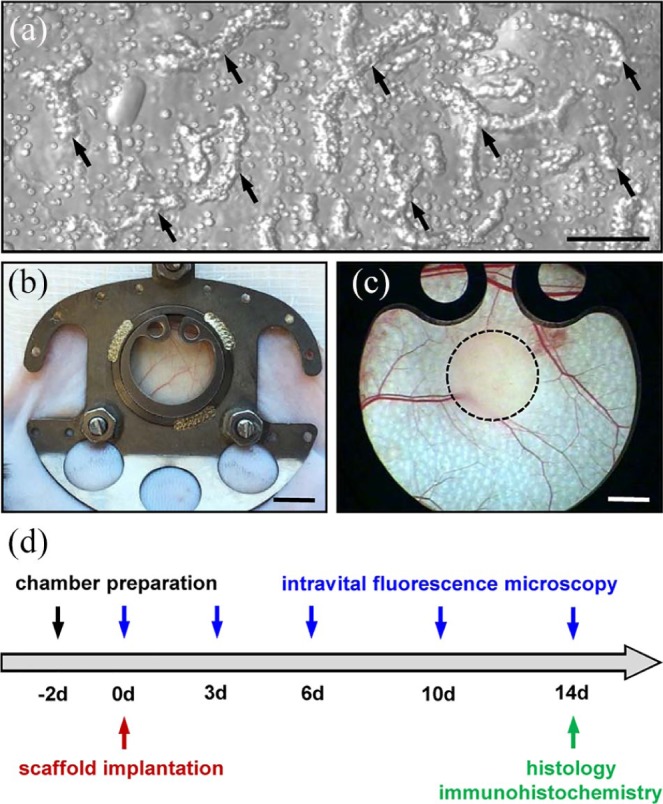
Model and experimental study design: (a) Brightfield microscopy of ad-MVFs (arrows) directly after enzymatic isolation from the epididymal fat pads of a GFP+ donor mouse. Scale bar: 80 µm. (b) Dorsal skinfold chamber on the back of a C57BL/6 mouse. Scale bar: 5 mm. (c) Stereomicroscopy of the observation window of a dorsal skinfold chamber after the implantation of an ad-MVF-seeded collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffold (borders marked by a broken line). Scale bar: 1.5 mm. (d) Time scheme of the dorsal skinfold chamber experiments. Two days after the chamber preparation, ad-MVF-seeded scaffolds were implanted and repetitively analyzed by means of intravital fluorescence microscopy on days 0, 3, 6, 10, and 14. Thereafter, the dorsal skinfold chamber tissue with the implants was excised and additionally analyzed by histology and immunohistochemistry.
