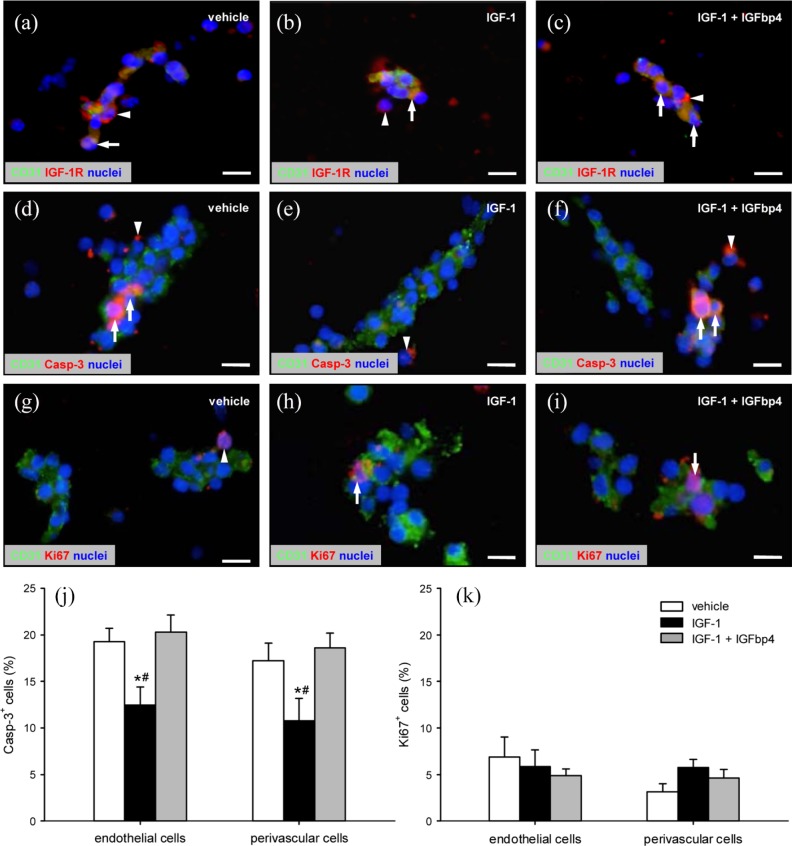
Figure 2.
IGF-1R expression, viability, and proliferative activity of ad-MVFs: (a–i) Fluorescence microscopy of fibrin-embedded ad-MVFs, which were cultivated for 24 h in 4°C UW solution supplemented with vehicle (a, d, g), IGF-1 (b, e, h), or a combination of IGF-1 and IGFbp4 (c, f, i). Staining was performed with Hoechst 33342 (a–i, blue) for the detection of cell nuclei and an antibody against CD31 (a–i; green) for the identification of endothelial cells in combination with an antibody against IGF-1R (a–c, red), an antibody against Casp-3 (d–f; red) for the labeling of apoptotic cells, or an antibody against Ki67 (g–i; red) for the labeling of proliferating cells. Arrows = marker-positive endothelial cells, arrowheads = marker-positive perivascular cells. Scale bars: 11 µm. (j) Casp-3+ apoptotic (%) and (k) Ki67+ proliferating (%) cells within ad-MVFs, which were cultivated for 24 h in 4°C UW solution supplemented with vehicle (white bars, n = 4), IGF-1 (black bars, n = 4), or a combination of IGF-1 and IGFbp4 (gray bars, n = 4).
Mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05 vs vehicle; #p < 0.05 vs IGF-1 + IGFbp4.