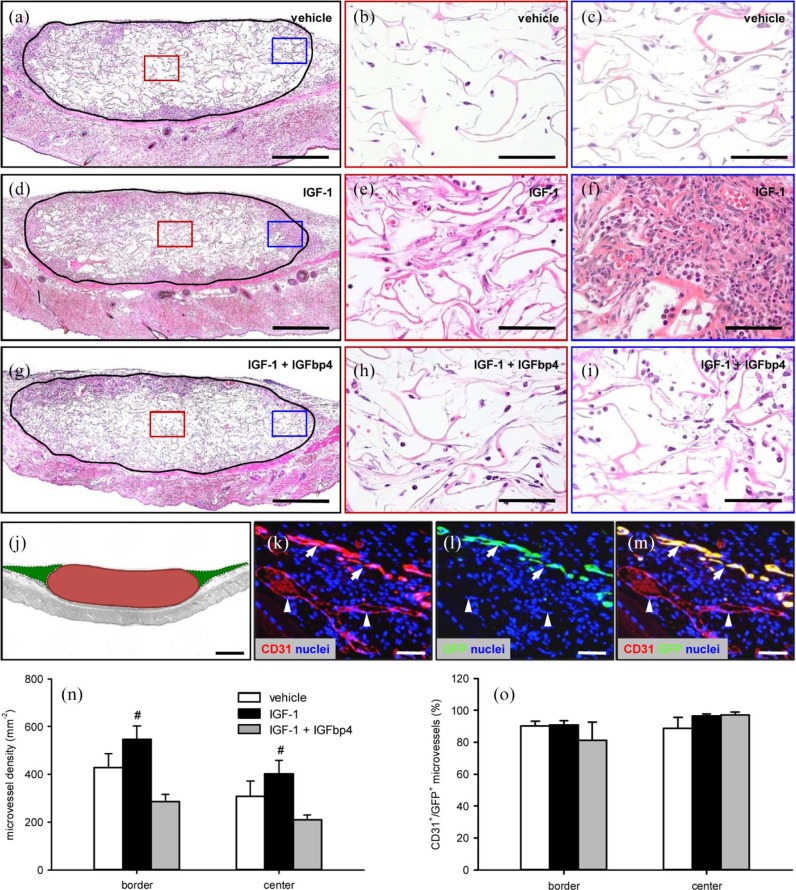
Figure 5.
Final vascularization and incorporation of ad-MVF-seeded scaffolds: (a–i): HE-stained sections of ad-MVF-seeded collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffolds (borders marked by closed line; b, e, h = red inserts in a, d, g; c, f, i = blue inserts in a, d, g) on day 14 after implantation into the dorsal skinfold chamber of C57BL/6 mice. The ad-MVFs were cultivated for 24 h in 4°C UW solution supplemented with vehicle (a–c), IGF-1 (d–f), or a combination of IGF-1 and IGFbp4 (g–i). Scale bars: a, d, g = 380 µm and b, c, e, f, h, i = 60 µm. (j): Scheme displaying the different areas, which were used for the immunohistochemical analyses (red = implanted scaffold (center) and green = surrounding host tissue (border)). Scale bar = 620 µm. (k–m): Representative images of immunohistochemically stained microvessels in the center of an ad-MVF-seeded collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffold on day 14 after implantation into the dorsal skinfold chamber of a C57BL/6 mouse. Staining was performed with Hoechst 33342 to identify cell nuclei (k–m, blue), an antibody against CD31 for the detection of endothelial cells (k, red) and an antibody against GFP (l, green). (m) The merge of (k) and (l). Arrows = CD31+/GFP+ microvessels and arrowheads = CD31+/GFP− microvessels. Scale bars: 70 µm. (n) Microvessel density (mm−2) and (o) CD31+/GFP+ microvessels (%) in the center and border zones of ad-MVF-seeded collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffolds 14 days after implantation into the dorsal skinfold chamber, as assessed by immunohistochemical analysis. The ad-MVFs were cultivated for 24 h in 4°C UW solution supplemented with vehicle (white bars, n = 8), IGF-1 (black bars, n = 8), or a combination of IGF-1 and IGFbp4 (gray bars, n = 8).
Mean ± SEM; #p < 0.05 vs IGF-1 + IGFbp4.