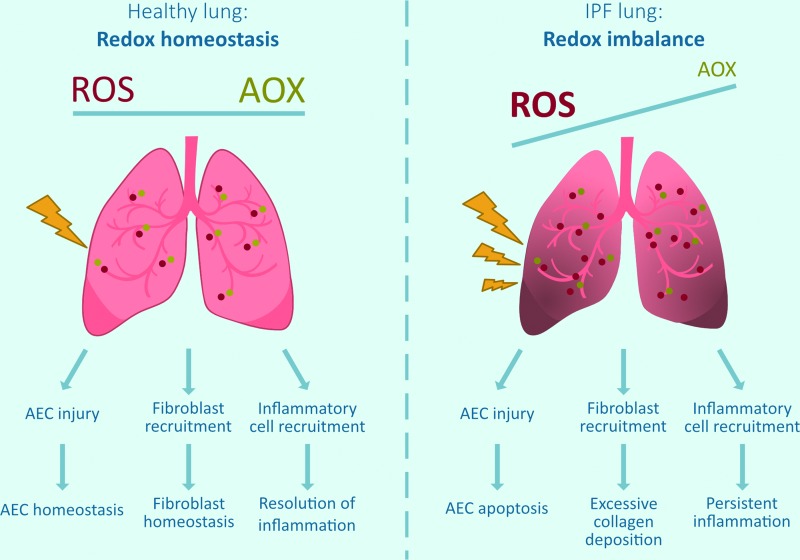
FIG. 1.
Altered lung redox homeostasis in IPF. In a healthy lung, there is a redox homeostasis, for example, ROS produced by exogenous or endogenous sources (mitochondria, NOXes, inflammatory cells) are appropriately countered by AOX. In IPF, there is a redox imbalance as ROS-generating processes are enhanced (increased NOX, mitochondrial dysfunction) and some antioxidant systems are compromised. This redox imbalance is thought to contribute to epithelial cell death, excessive collagen deposition, and persistent inflammation, resulting in pulmonary fibrosis and tissue scarring. AEC, alveolar epithelial cell; AOX, antioxidants; IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; NOXes, NADPH oxidases; ROS, reactive oxygen species. Color images are available online.