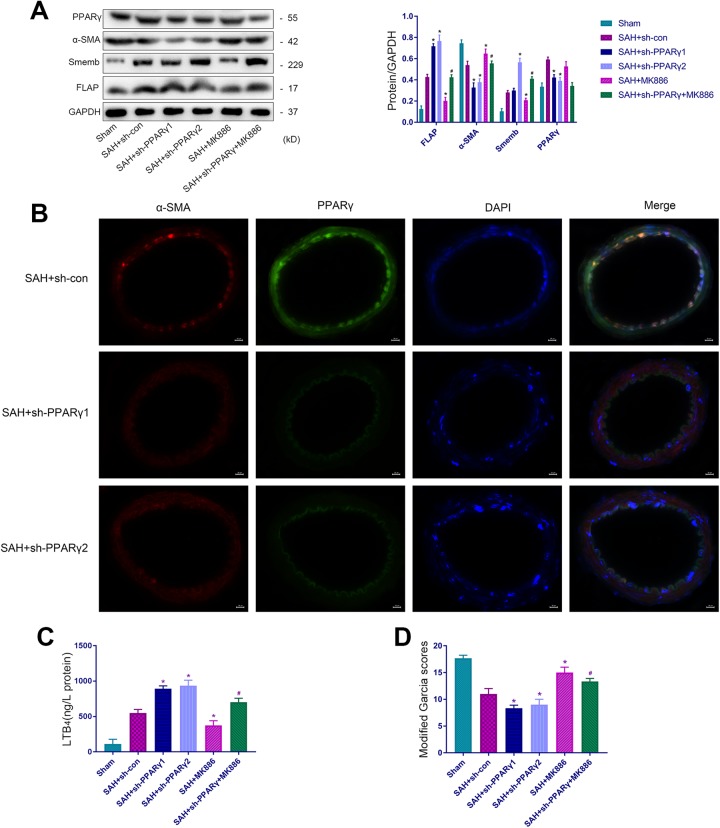
Figure 4.
PPARγ activation inhibits the phenotypic transformation of VSMCs partially by suppressing FLAP/LTB4 expression. (A) Representative immunoblots and representative quantitative analyses of α-SMA, Smemb, PPARγ and FLAP. (B) Representative IF staining of the middle cerebral artery for α-SMA (red), PPARγ (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) The expression of LTB4. (D) Modified Garcia scores in Sham, SAH+sh-con, SAH+sh-PPARγ1, SAH+sh-PPARγ2, SAH+MK-886, and SAH+sh-PPARγ+MK-886 groups (*p<0.05 versus SAH+si-con group, # p<0.05 versus SAH+sh-PPARγ2 group). (D) (n=12, with 12 used for modified Garcia scores, 6 used for Western blotting and ELISA and 6 used for IF).
α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FLAP: 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein; IF, immunofluorescence; LTB4: leukotriene B4; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage; Smemb: embryonic smooth muscle myosin heavy chain; VSMC: vascular smooth muscle cell.