Figure 1.
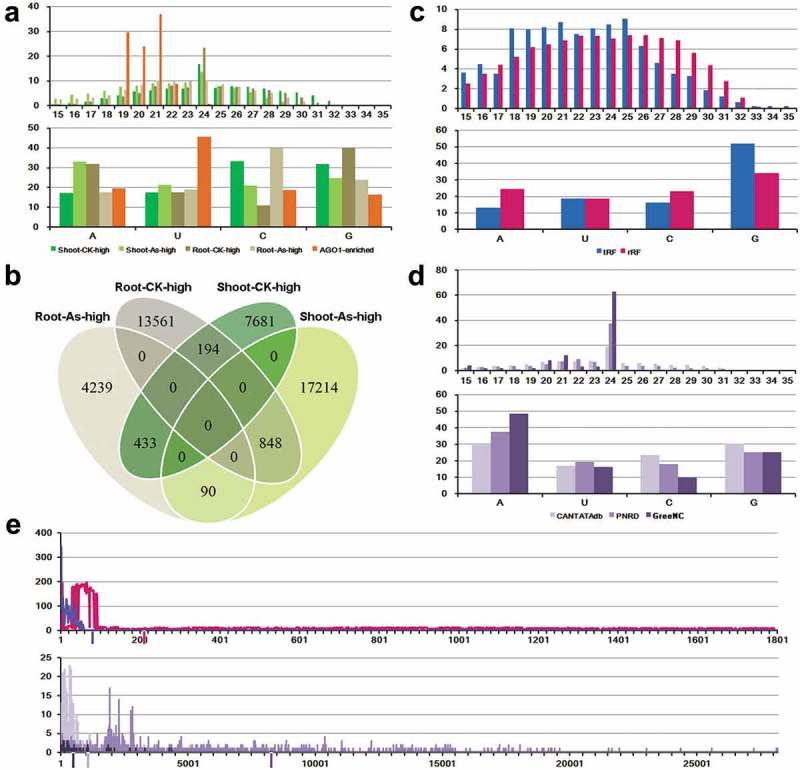
Sequence characteristics of the rice small RNAs responsive to arsenic stress. (a) Sequence length distribution and 5ʹ terminal nucleotide composition of arsenic-responsive small RNAs (sRNAs). Shoot-CK-high: sRNAs repressed in shoots under arsenic stress. Shoot-As-high: sRNAs induced in shoots under arsenic stress. Root-CK-high: sRNAs repressed in roots under arsenic stress. Root-As-high: sRNAs induced in roots under arsenic stress. AGO1-enriched: arsenic-responsive sRNAs that are enriched in AGO1 complexes. (b) Venn diagram showing the overlaps among the four categories of arsenic-responsive sRNAs. (c) Sequence length distribution and 5ʹ terminal nucleotide composition of arsenic-responsive sRNAs mapped onto tRNAs or rRNAs. tRF: arsenic-responsive sRNAs mapped onto tRNAs. rRF: arsenic-responsive sRNAs mapped onto rRNAs. (d) Sequence length distribution and 5ʹ terminal nucleotide composition of arsenic-responsive sRNAs mapped onto the rice long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). CANTATAdb: arsenic-responsive sRNAs mapped onto lncRNAs registered in CANTATAdb. PNRD: arsenic-responsive sRNAs mapped onto lncRNAs registered in PNRD. GreeNC: arsenic-responsive sRNAs mapped onto lncRNAs registered in GreeNC. In (a,c,d) the Y axes measure the percentages of the sRNAs. (e) Enrichment of arsenic-responsive sRNA loci towards the 5ʹ half of tRNAs (blue), rRNAs (pink), CANTATAdb-registered lncRNAs (light purple), PNRD-registered lncRNAs (purple), and GreeNC-registered lncRNAs (dark purple). The average length of each RNA species was denoted by the vertical bar with the representative color below the X-axis. Y axes indicate the number of the arsenic-responsive sRNAs mapped onto each position of the tRNAs, rRNAs or lncRNAs.
