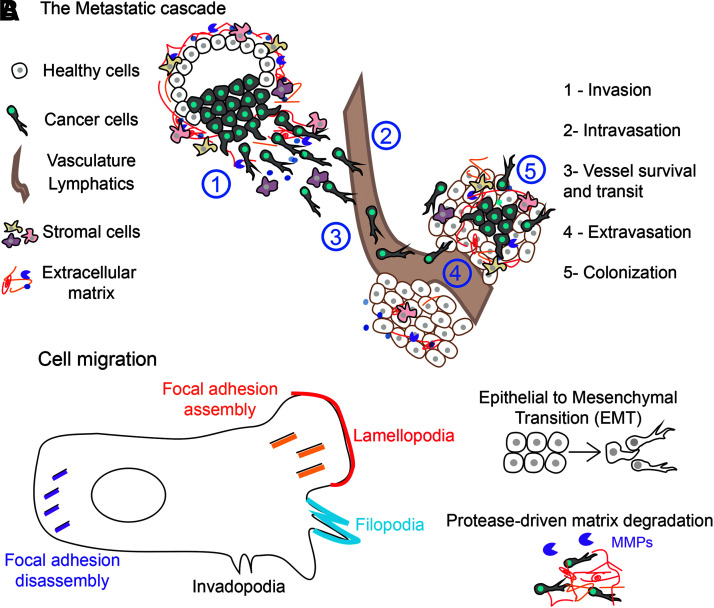
FIG. 1.
The metastatic cascade and cancer cell migration. (A) Metastasis involves five main steps: local invasion into surrounding tissue, intravasation into the vasculature or lymphatics, survival and transit in the vessels, extravasation into a secondary tissue, and colonization. (B) Cancer cell migration, which is important for all stages of metastasis, includes but is not limited to focal adhesion assembly at the leading edge/disassembly at the trailing edge, formation of invadopodia, lamellipodia, and filopodia, the EMT process, and protease-driven ECM degradation. ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial to mesenchymal transition.