Fig. 4|. De novo NAD+ synthesis regulates basal and LPS-activated macrophage polarization, immune factor generation, and phagocytosis.
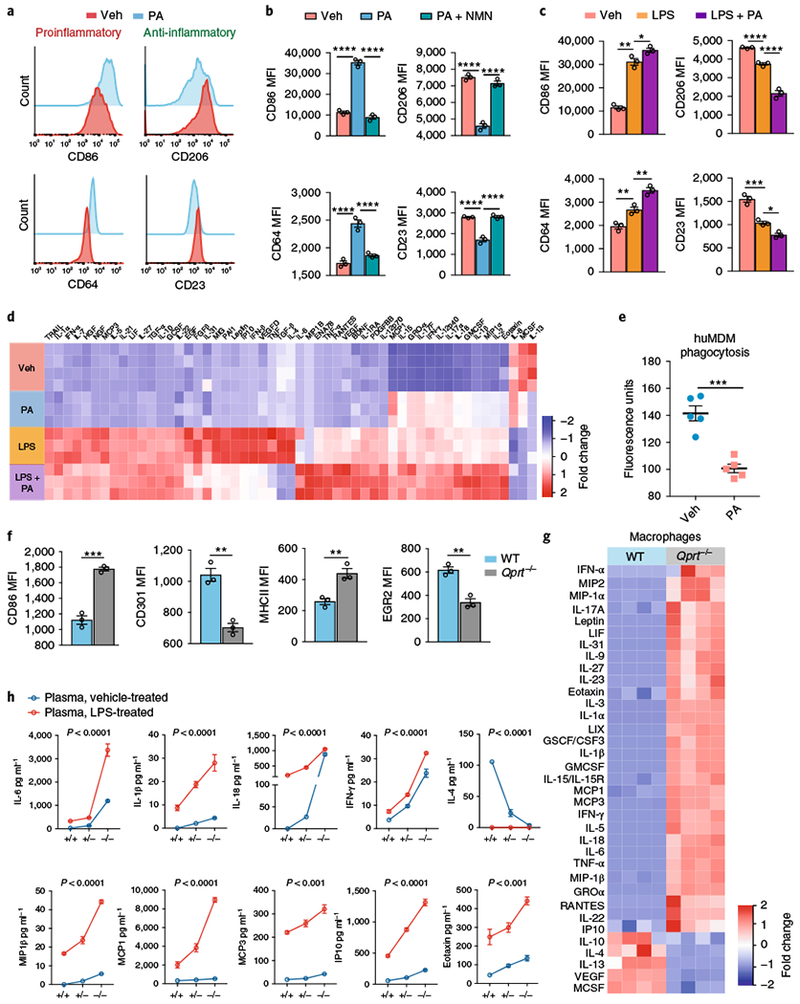
a–e Human MDMs were treated with the QPRT inhibitor PA (500 μM, 20 h) ± NMN (10 μM, 20 h) or ± LPS and assayed by flow cytometry for inflammatory surface markers and immune factors using Luminex multi-analyte measurements. a, Representative histograms of three independent experiments for the proinflammatory markers CD86 and CD64 and anti-inflammatory markers CD206 and CD23 in resting macrophages stimulated with PA. See Supplementary Fig. 5a,b. b, MFIs were quantified in human MDMs treated with PA and NMN; n = 3 biologically independent samples per group, 7,300–11,200 cells per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. c, MFIs for proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers in LPS-stimulated macrophages treated with PA; n = 3 biologically independent samples per group, 7,200–13,358 cells per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. See Supplementary Fig. 5c. d, Hierarchical clustering of immune factors in culture medium of human MDMs ± PA and ± LPS (n = 4 per group; P < 0.05 by ANOVA). See also Supplementary Figure 5d. e, Phagocytosis of fluorescein-labeled E. coli in human MDMs treated with PA or vehicle; n = 5 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; ***P = 0.0002, two-tailed Student’s t-test. f, WT and Qprt−/− peritoneal macrophages were assayed by flow cytometry for proinflammatory CD86 and major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) and anti-inflammatory CD301 and early growth response protein 2 (EGR2); n = 3 biologically independent samples per group, 2,145–3,224 cells per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; **P < 0.01, ***P <0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. g, Hierarchical clustering of immune factors produced by peritoneal macrophages from WT and Qprt−/− mice 20 h after isolation. h, WT and Qprt−/− mice were systemically stimulated with either vehicle or LPS (5 mg kg−1, intraperitoneal injection) and plasma was assayed at 20 h for immune factors. n = 3 biologically independent samples for the WT group, n = 4 biologically independent samples for the Qprt−/− group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m. The two-way ANOVA effect of LPS is P < 0.0001 for all immune factors; the effect of genotype is P < 0.0001 for all immune factors except for monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1) and eotaxin, where P < 0.001.
