Fig. 8|. De novo NAD+ synthesis is reduced in aging human MDMs and in vivo in aging mouse macrophages.
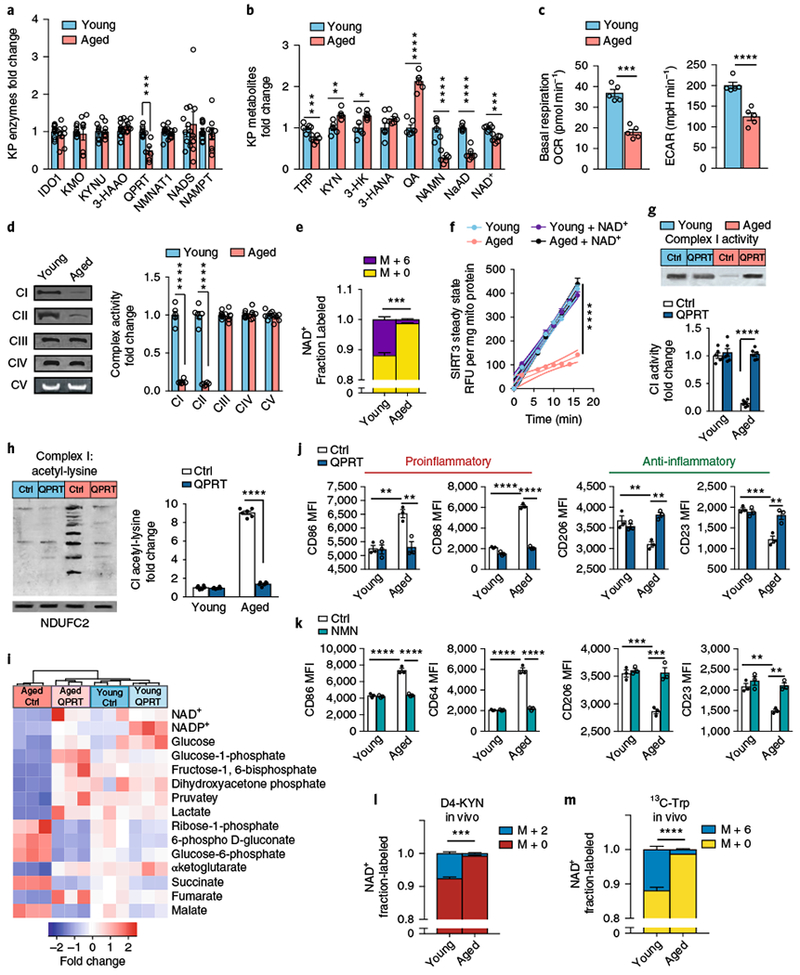
a–f, Young and aged human MDMs were derived from individuals ≤35 and ≥65 years old, respectively, and analyzed for QPRT levels, KP and NAD+ metabolites, mitochondrial respiration, and immune polarization state. See Supplementary Figs. 9,10. a, Quantitative immunoblot analysis of human MDMs of QPRT expression in aging versus young macrophages; n = 9 biologically independent samples per group for IDO1 and NADS, n = 10 biologically independent samples per group for 3-HAAO, n = 8 biologically independent samples per group for all other enzymes, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; ***P = 0.0006, two-tailed Student’s t-test. b, LC-MS quantification of KP metabolites, NAD+ precursors, and NAD+ in young versus aged macrophages; n = 6 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. c, Basal respiration and ECAR in young compared to aged macrophages; n = 5 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; ***P = 0.0002, ****P < 0.0001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. d, Left: representative BN-PAGE blot of complex I and II activities in young versus aged human MDMs. Right: quantification of complex activities; n = 6 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; ****P < 0.0001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. e, 13C-Trp was added to young and aged human MDMs and the fraction of labeled M+6 NAD+ was quantified with LC-MS; n = 3 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; ***P = 0.0004, two-tailed Student’s t-test. f, Young and aged human MDMs were assayed for SIRT3 steady-state activity; n = 6 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; the curved thin lines denote 95% CIs; ****P < 0.0001 via linear regression analysis. g-j, Young and aged human MDMs were transfected with either control vector (Ctrl) or QPRT vector (QPRT) and assayed for complex activities, targeted metabolomics, and immune polarization. g, Top: representative BN-PAGE blot of complex I activity in young and aged human MDMs transfected with either control or QPRT vectors. Bottom: quantification of complex I activity; n = 6 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; two-way ANOVA, effect of age and QPRT, ****P < 0.0001; Tukey’s post hoc test, ****P < 0.0001. h, Left: representative 2D SDS blot of complex I from young and aged human MDMs ± QPRT overexpression assayed for acetyl-lysines. Right: quantification of acetyl-lysines in complex I; n = 6 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; two-way ANOVA, effect of age and QPRT, ****P < 0.0001; Tukey’s post hoc test, ****P < 0.0001). i, Hierarchical clustering of targeted metabolomics in young versus aged human MDMs transfected with control or QPRT vector (n = 3 biologically independent samples per group). j, MFIs of the proinflammatory markers CD86 and CD64 and anti-inflammatory markers CD206 and CD23 in aged and young human MDMs transfected with control or QPRT vector. N = 3 biologically independent samples per group, 8,374–12,576 cells per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; two-way ANOVA effect sizes: CD86, effect of age and QPRT, P < 0.01; CD64, effect of age and QPRT, P < 0.0001; CD206, effect of QPRT, P < 0.01; CD23, effect of age, P < 0.001, and effect of QPRT, P<0.01; Bonferroni post hoc test: **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. k, Effect of NMN supplementation (10 μM, 20 h). N = 3 biologically independent samples per group, represented as the mean ± s.e.m.; two-way ANOVA effect sizes: CD86, effect of age and NMN, P < 0.0001; CD64, effect of age and NMN, P < 0.0001; CD206, effect of age and NMN, P < 0.001; CD23, effect of age and NMN, P < 0.01; Bonferroni post hoc test: **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. l-m, De novo NAD+ synthesis is reduced in aging mouse macrophages in vivo; n = 3 biologically independent samples per group; ***P = 0.0002 and ****P < 0.0001 for young versus aged, two-tailed Student’s t-test. Young (3 months) and aged (16–18 months) C57B/6J mice were administered 8 mg of D4-KYN (l) or 13C-Trp (m) by oral gavage, and de novo NAD+ levels were measured in peritoneal macrophages 4 h later with LC-MS. Data are represented as the mean ± s.e.m.
