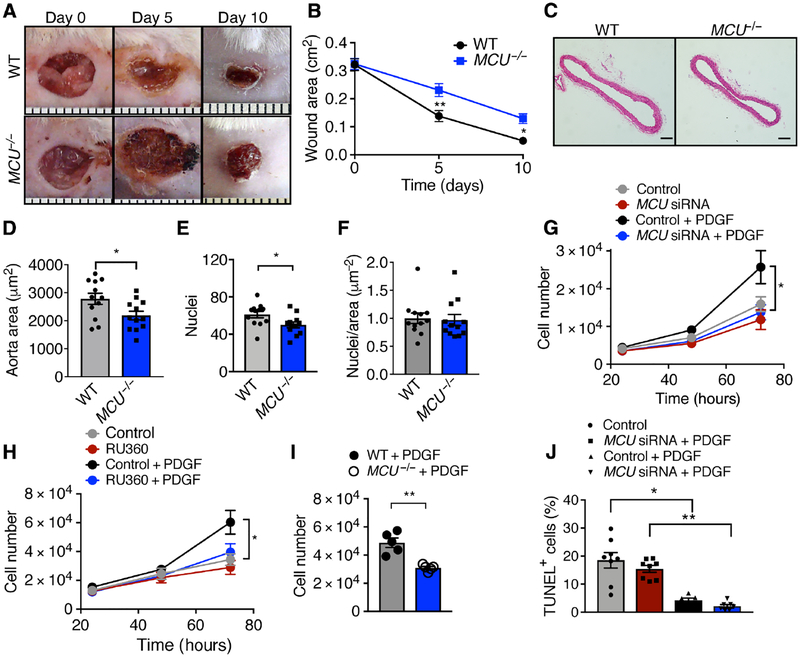
Figure 1. Deletion of MCU reduces cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro.
A) Interscapular wounds after skin punch in WT and MCU−/− mice. B) Quantification of wound area. n = 8 mice per genotype. C) H&E-stained cross sections of the descending aorta. Scale bar = 100 μm. D) Quantification of aortic medial cross-sectional areas. n = 12 mice per genotype. E) Quantification of cell nuclei in the aortic media. F) Ratio of nuclei per area, derived from E and D. G) Cell counts for cultured VSMCs transfected with MCU or scrambled siRNA in growth medium with 20 ng/mL PDGF. n = 9 independent experiments. H) Cell counts for VSMCs treated with the MCU inhibitor RU360 (100 nM) and/or PDGF. n = 8 independent experiments. I) Cell counts for skin fibroblasts from MCU−/− or WT mice at 72 h in growth medium with 20 ng/mL PDGF. n = 7 independent experiments. J) TUNEL-staining in VSMCs transfected with MCU or scrambled siRNA and treated with 20 ng/mL PDGF for 48 h. n = 6 independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.001 by 2-Way repeat measure ANOVA (B), Mann-Whitney test (D, F, I), two-tailed t-test (E), 1-way ANOVA at 48 h (G, H), Kruskal-Wallis test (J).