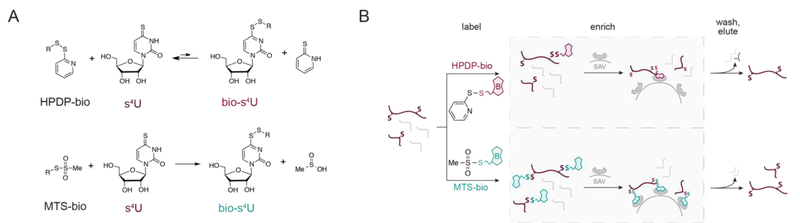
Figure 3:
Significance of inefficient chemistry toward length bias in s4U metabolic labeling experiments. (A) Chemistry of activated disulfide reactivity with s4U. When HPDP-biotin is used as the activated disulfide, any biotin-s4U (bio-s4U) product results in a more activated disulfide due to the electron-poor pyrimidine ring of s4U, therefore favoring the reverse rather than the forward biotinylation reaction. In contrast, MTS-biotin reacts irreversibly with s4U to form the bio-s4U product under the reaction conditions, and the covalent disulfide bond can only be reversed under reducing conditions. (B) Schematic of s4U-RNA enrichment with HPDP- and MTS-biotin. Efficient activated disulfide reactivity of MTS-biotin results in greater yields of s4U-RNA and alleviates potential biases toward longer RNAs with more uridines.