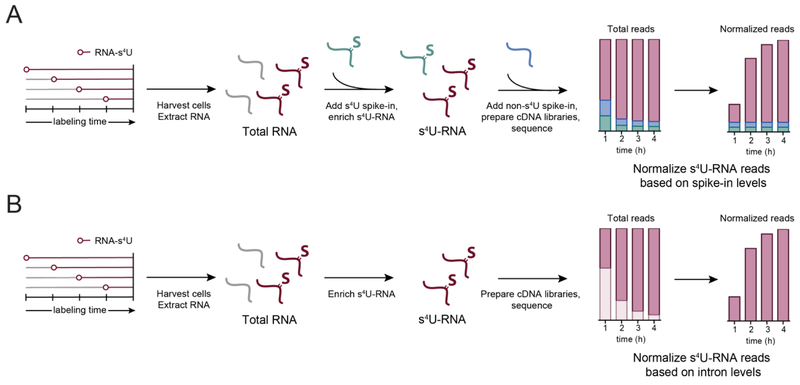
Figure 4:
Methods to normalize s4U-RNA data after high-throughput sequencing. (A) After cells are metabolically labeled with s4U and total RNA is extracted, exogenous s4U-RNA (s4U-labeled RNA from S. pombe, or in vitro-transcribed s4U-RNAs) are added to each sample and then enriched. Alternatively or in addition, exogenous RNA without s4U can also be added to samples after enrichment. Samples are then analyzed by high-throughput sequencing and normalized based on the number of reads that align to the spike-in sample. (B) Samples can also be enriched without RNA spike-ins and normalized based on the relative proportion of introns in each sample (Lugowski et al., 2018). First, intron coverage for each transcript is determined based on the number of reads that map to introns in the longest isoform of a given transcript without overlapping exons or any other isoform. Next, introns are filtered for coverage and time-dependent changes in expression. Reads that map to exons are finally normalized to the sum of all reads mapping to the well-behaved intron set.