FIGURE 4.
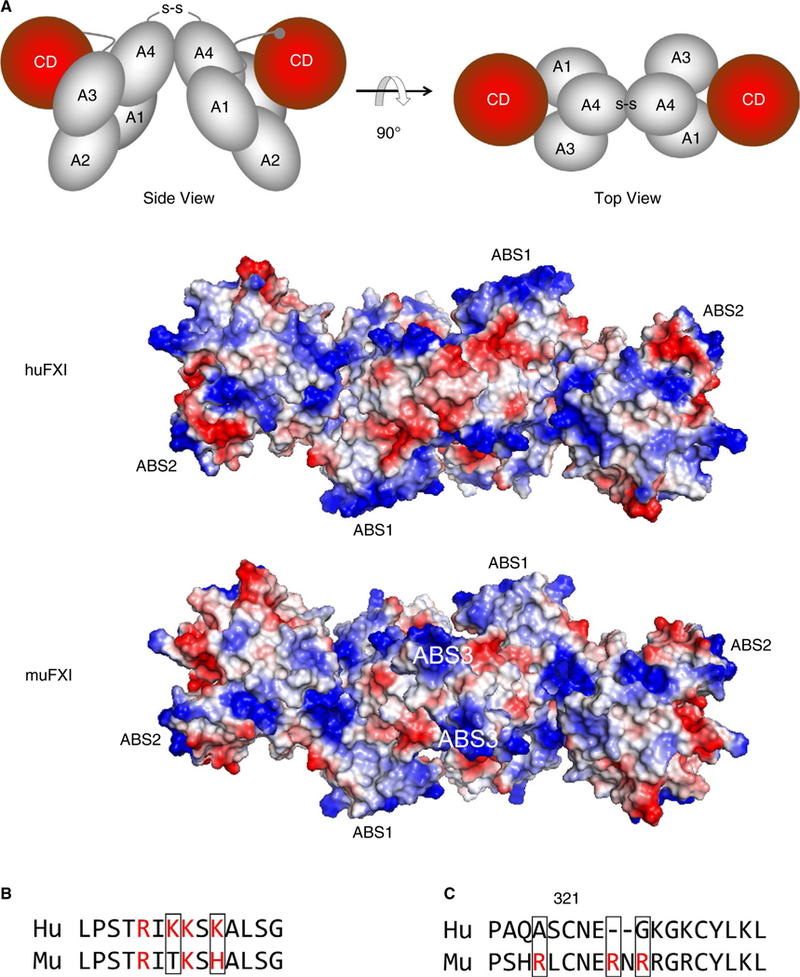
FXI anion binding sites (ABSs). (A) The images at the top are schematic representations of the human FXI dimer based on the crystal structure reported by Papagrigoriou et al7 in “side view” (left) and rotated 90 degrees for a “top view (right). The four apple domains (A1-A4) and catalytic domains (CD [red]) are shown. The disulfide bond (S-S) between Cys321 on each A4 domain indicates the position of the dimer interface. The RGB structural images below the schematic diagrams depict top views of huFXI and muFXI FXI dimers, with positively charged regions indicated in blue and negatively charged regions in red. Positions of ABS1 and ABS2 for both species, and ABS3 in muFXI are indicated. The three ABSs are positioned in a roughly linear arrangement, crossing the dimer interface created by the A4 domains. (B) A comparison of the amino acid sequences in ABS1 on the Apple 3 domain in human (Hu) and mouse (Mu) FXI. Basic residues are indicated in red. (C) Amino acid sequences of human (Hu) and murine (Mu) FXI in the Apple 4 domain in the vicinity of Cys321. Basic residues are indicated in red
