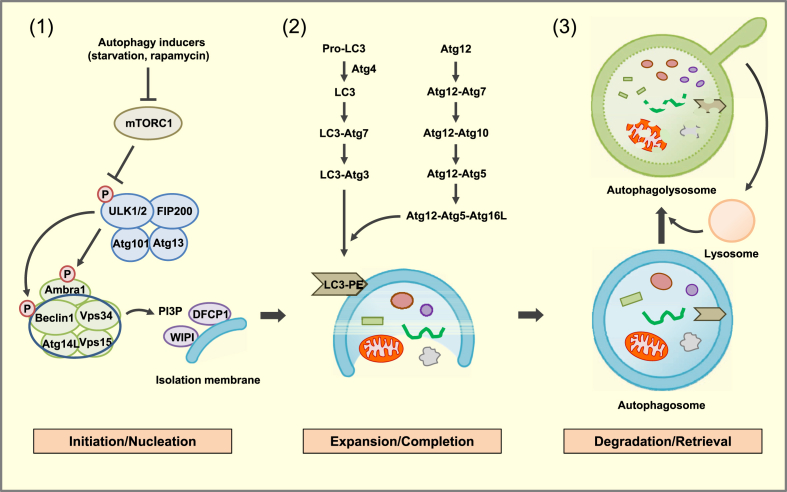
Figure 1.
Molecular pathways of autophagy. (1) Initiation/Nucleation: Autophagy inducers such as nutrient deprivation or rapamycin reduce mTORC1 phosphorylation, which liberates the ULK1/2 complex. The ULK1/2 complex increases activity of the Beclin1/Vps34 complex through phosphorylation of Ambra1 and Beclin 1. PI3P, produced by Vps34, recruits effector proteins such as DFCP1 and WIPI2 to promote formation of isolation membrane and to constitute the nucleation step. (2) Expansion/Completion: Expansion of autophagosome is mediated by two conjugated systems comprising Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L and LC3-Atg3 which lead to the formation of LC3-PE (LC3-II). (3) Degradation/Retrieval: After completion, mature autophagosome fuses with lysosome forming autophagolysosome, wherein the sequestered materials or organelles are degraded by lysosomal enzymes. After digestion of entrapped materials, nutrients become available and mTORC1 is reactivated. Proto-lysosomal tubules are then formed which mature into functional lysosome, constituting the retrieval process.