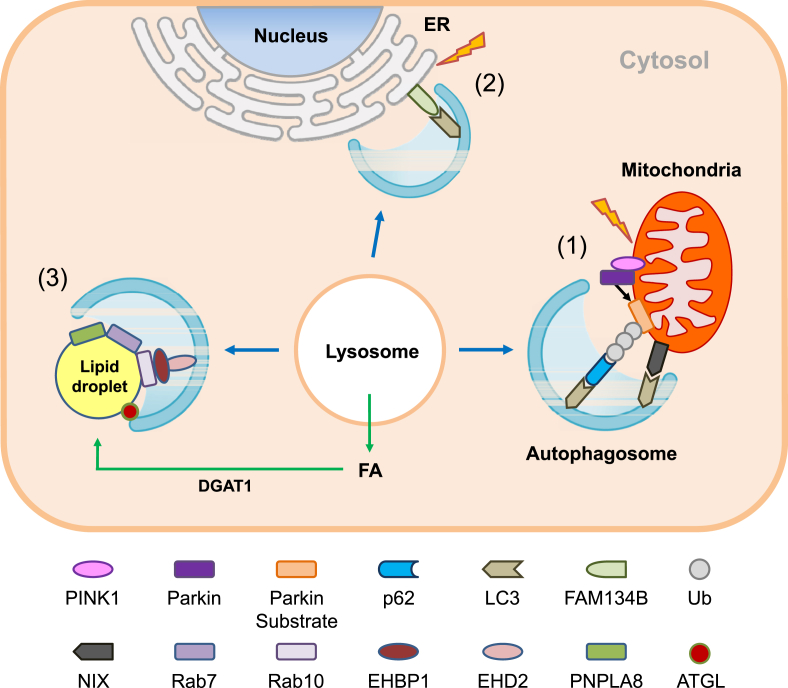
Figure 2.
Machinery of selective autophagy. (1) Mitophagy: When mitochondrial potential is dissipated by mitochondrial stressors, PINK1 is stabilized on the outer membrane of mitochondria and recruits Parkin. Parkin, as an E3 ligase, ubiquitinates several substrates in mitochondria and induces mitophagy together with autophagy receptors including p62, optineurin, NDP52 and NBR1. In addition to Parkin-mediated ubiquitin-dependent mitophagy, Parkin-independent receptor-mediated autophagy and piecemeal-type mitophagy has also been described. (2) ER-phagy: An ER membrane protein, FAM134B, has been shown to mediate ER-phagy through the interaction of the LIR domain of FAM134B and LC3. In addition to FAM134B, Sec62 and RTN3 can also interact with LC3 through their LIR domains. FAM134B and Sec62 mediate ER-phagy of ER cistern, while RTN3 mediates that of ER tubule. (3) Lipophagy: Small GTPases such as Rab7 or Rab10 have been shown to mediate the formation of the ‘lipophagic synapse’ and autophagic degradation of LD. LC3 may also facilitate recruitment of ATGL to LD via the interaction with the LIR domain of ATGL, leading to lipolysis by cytosolic lipases. Autophagy may also contribute to the DGAT-1-dependent formation of LD by providing free fatty acids (FFAs) (green arrows), which may favor efficient oxidative degradation of FFAs through β-oxidation after transfer to mitochondria and reduce lipotoxicity of FFAs.