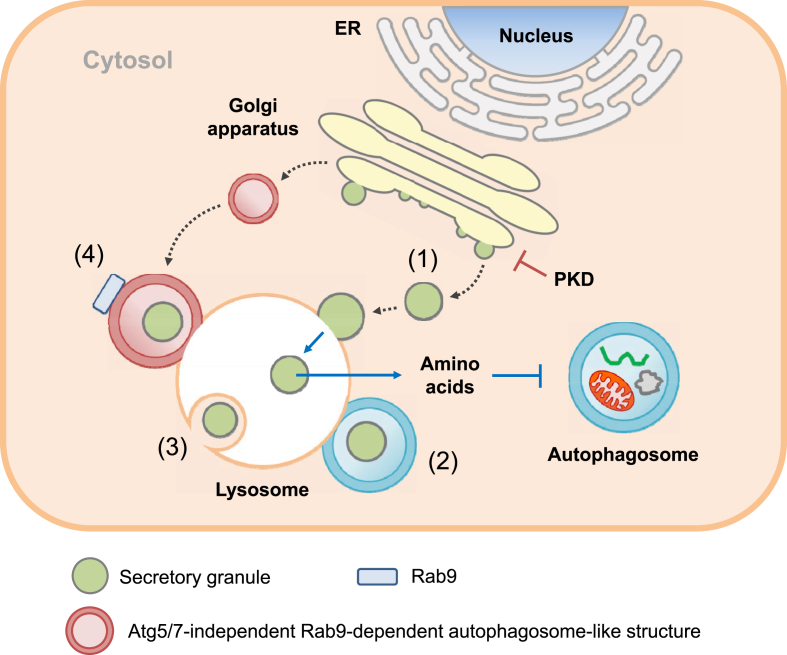
Figure 4.
Lysosomal autophagic degradation pathways other than macroautophagy in pancreatic β-cells. (1) SINGD: In starvation, PKD is inactivated at the Golgi area and nascent insulin secretory granules generated in Golgi apparatus directly fuse with lysosomes. Amino acids released from lysosomal degradation of insulin secretory granules inhibit autophagy through mTORC1. (2) Vesicophagy: Insulin granules are sequestered in autophagosome, and autophagosome containing insulin secretory granules as an autophagy cargo fuses with lysosome for degradation of insulin secretory granules. (3) Microautophagy: β-cell granules are engulfed by late endosome or multivesicular body in a manner similar to phagocytosis for degradation of the granule components. (4) GOMED: When the insulin secretory process from the Golgi apparatus is suppressed in autophagy-deficient β-cells, autophagosome-like double-membrane compartment is formed from Golgi membrane in an Atg5/7-independent but Rab9-dependent manner.