Figure 1.
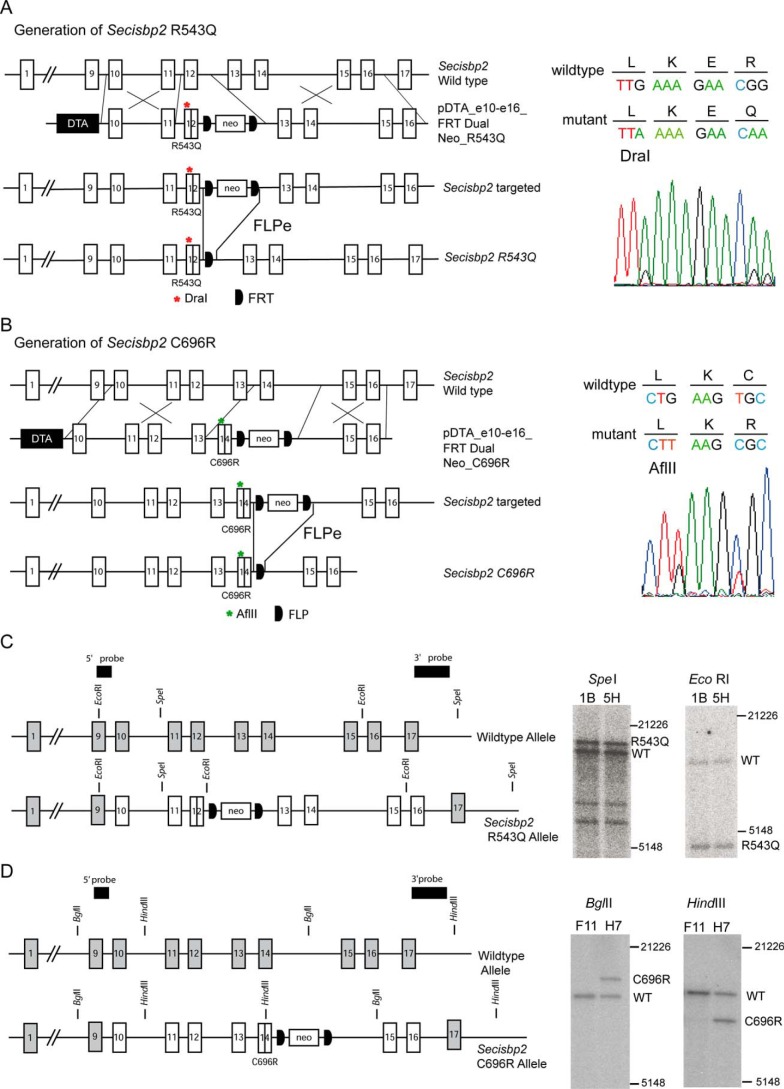
Generation of Secisbp2 alleles in mice carrying pathogenic mutations found in patients. A, strategy to build the targeting vector containing a R543Q mutation in exon 12 and a FRT-flanked neo cassette in intron 12 for double homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. After germline transmission, the neo cassette is removed by germline FLPe expression. Sanger sequencing confirmed the heterozygous base substitutions in the Arg-543 codon and in the Leu-540 codon, creating a diagnostic DraI restriction site. DTA refers to a diphtheria toxin A chain used for negative selection against off-site integration. B, strategy to build the targeting vector containing a C696R mutation in exon 14 and a FRT-flanked neo cassette in intron 14 for double homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. After germline transmission, the neo cassette is removed by germline FLPe expression. Sanger sequencing confirmed the heterozygous base substitutions in the Cys-696 codon and in the Leu-694 codon creating a diagnostic AflII restriction site. C and D, verification of correct gene targeting by Southern blotting using hybridization probes located outside of the targeting vector sequence. C, Secisbp2 R543Q allele. The SpeI digestion was combined with the 3′ probe and yielded the expected fragments of 12,148 bp (WT) and 14,048 bp (RQ). The EcoRI digestion was combined with the 5′ probe and yielded fragments of 9129 bp (WT) and 4209 bp (RQ). D, Secisbp2 C696R allele. The BglII digestion was combined with the 5′ probe and yielded the expected fragments of 8328 bp (WT) and 10,228 bp (CR). The HindIII digestion was combined with the 3′ probe and yielded the expected fragments of 10,177 bp (WT) and 7340 bp (CR). DNA marker sizes in bp are indicated.