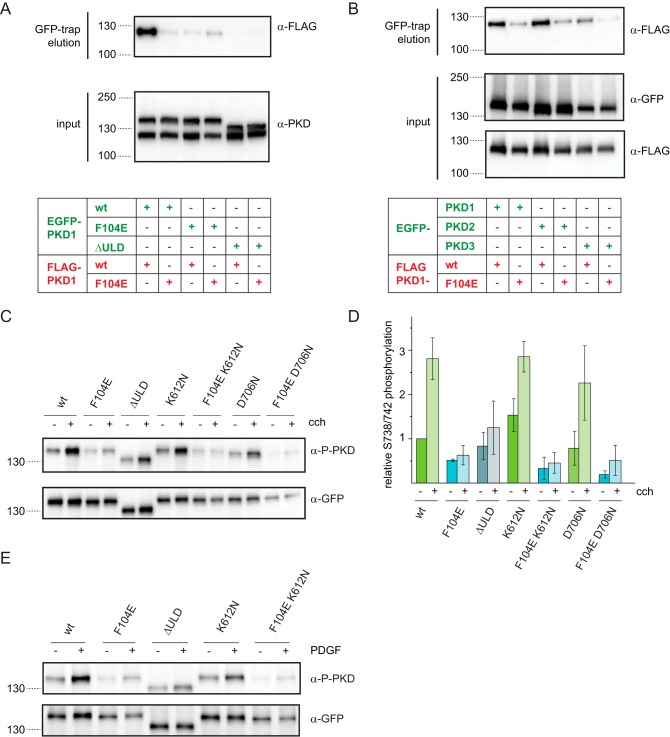
Figure 5.
ULD dimerization is required for PKD activation in cells. A, EGFP- and FLAG-tagged PKD1 constructs were co-expressed in HEK293T cells and subjected to co-immunoprecipitation using GFP-trap. Expression levels of transgenes and co-immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by Western blotting using a PKD-specific antibody (α-PKD) and FLAG tag–specific antibody (α-FLAG), respectively. The blot is representative of three biological replicates. B, FLAG-tagged PKD1 and PKD1F104E were co-expressed with EGFP-tagged PKD1, PKD2, and PKD3 in HEK293T cells. Lysates were probed for expression levels by Western blotting using GFP-specific and FLAG-specific antibodies (α-GFP and α-FLAG, respectively). Co-immunoprecipitate (GFP-trap) was probed with a FLAG-specific antibody. The figure is representative of three independent experiments. C, HEK293T cells expressing EGFP-PKD1 constructs were stimulated with 10 μm carbachol for 15 min at 37 °C. Western blotting shows activation loop phosphorylation at Ser738/Ser742 (α-P-PKD) as well as EGFP-PKD1 expression levels (α-GFP). K612N and D706N are two different kinase-dead versions of PKD. D, quantification of C by densitometry. Activation loop phosphorylation signal (α-P-PKD) was divided by the total EGFP-PKD1 signal (α-GFP) and normalized to unstimulated WT. Mean and S.D. (error bars) are derived from three independent experiments. E, NIH3T3 cells expressing the same EGFP-PKD1 constructs as in C were stimulated with 1 μm human PDGF-BB (50 ng/ml) for 30 min at 37 °C. PKD activation was assessed by Western blotting using phospho-Ser738/Ser742–specific antibody (α-P-PKD). Expression levels were probed with GFP-specific antibodies. The blots are representative of three independent experiments.