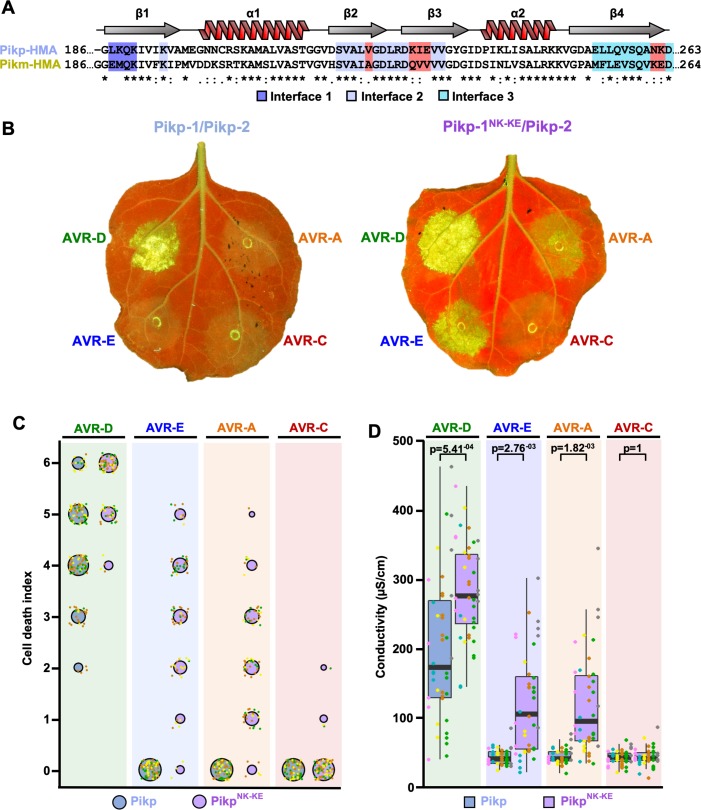
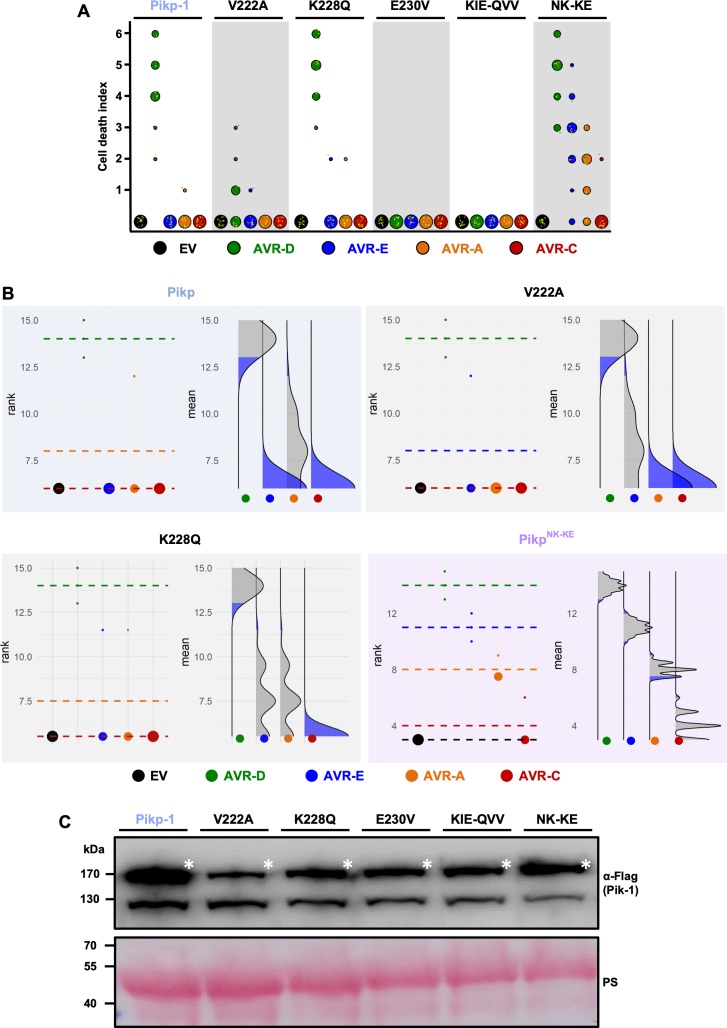
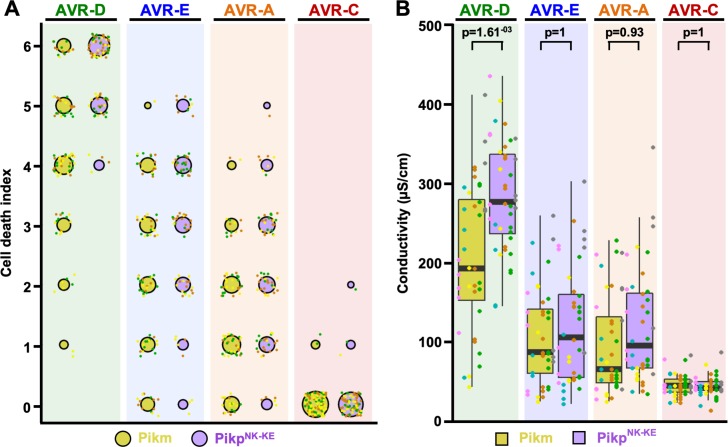
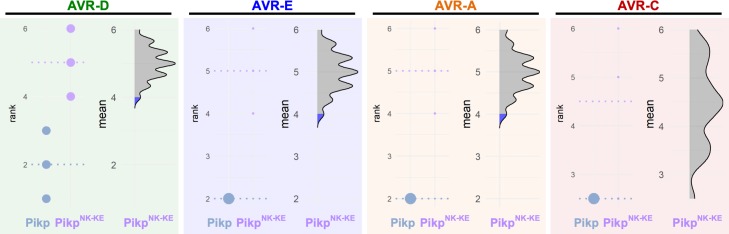
Figure 1. Structure-informed engineering expands Pikp-mediated effector recognition in N. benthamiana.
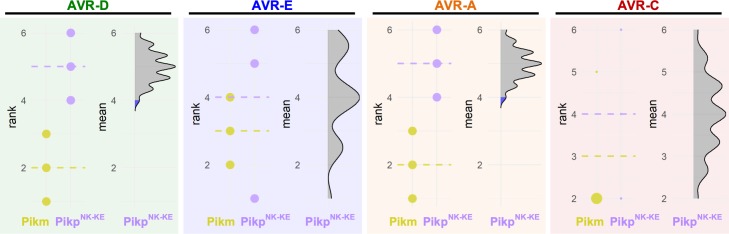
(A) Sequence alignment of the Pikp-1 and Pikm-1 HMA domains. Secondary structure features of the HMA fold are shown above, and the residues that are located at binding interfaces are as colored. Key residues from interface 2 and interface 3 involved in this study are highlighted in red. (B) Representative leaf images showing Pikp- (left) or Pikp-1NK-KE (right)-mediated cell death in response to AVR-Pik variants as autofluorescence under UV light. (C) Autofluorescence intensity is scored as previously described (Maqbool et al., 2015; De la Concepcion et al., 2018). Cell death assay scores are represented as dot plots for Pikp and PikpNK-KE (blue and purple, respectively). For each sample, all of the data points are represented as dots with a distinct color for each of the three biological replicates; these dots are plotted around the cell death score for visualization purposes. The size of the centre dot at each cell death value is directly proportional to the number of replicates in the sample with that score. The total number of repeats was 80. Data for Pikp have been previously shown (De la Concepcion et al., 2018), but was acquired at the same time as those for PikpNK-KE. The estimation methods used to visualize differences in the data sets are shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 3. (D) Conductivity measurements showing ion leakage as a quantitative measure of cell death. The centre line represents the median, the box limits are the upper and lower quartiles, the whiskers extend to the largest value within Q1 – 1.5x the interquartile range (IQR) and the smallest value within Q3 + 1.5x IQR. All the data points are shown as dots with distinct colors for each biological replicate. For each experiment, six biological replicates with 5 or 10 internal repeats were performed (total data points = 40). ‘p’ is the p-value obtained from statistical analysis and Tukey’s HSD (honestly significant difference) test.