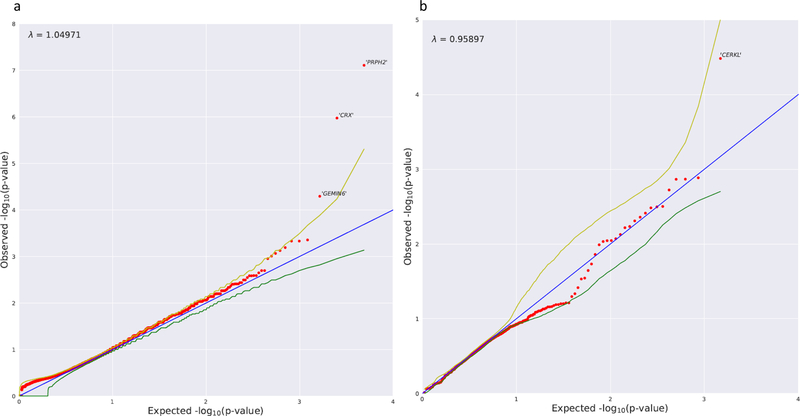
Fig. 2. Dominant model and recessive nonsynonymous model collapsing analysis results.
(a) Quantile–quantile (QQ) plot for exome-wide gene-based collapsing analysis under the dominant genetic model. The y-axis represents the –log10 of the observed Fisher’s exact test (FET) p values (sorted). The x-axis represents the –log10 of the permutation-based expected FET p values (sorted). The red dots represent the data points, while the blue line is the diagonal with slope 1. The green and yellow lines represent permutation-based 95% confidence intervals. Data points falling outside the 97.5th percentile bound are labeled with corresponding gene symbols. PRPH2 and CRX reached study-wide significance. (b) QQ plot for the collapsing analysis under the recessive n model. The y-axis represents the –log10 of the observed p values (sorted) evaluated in the Firth logistic regression adjusting for the first ten ancestry principal components. The x-axis represents the –log10 of the expected p values (sorted) evaluated in the same logistic regression model with permutation (“BiasedUrn”). The red dots represent the data points, while the blue line is the diagonal with slope 1. The green and yellow lines represent permutation-based 95% confidence intervals.