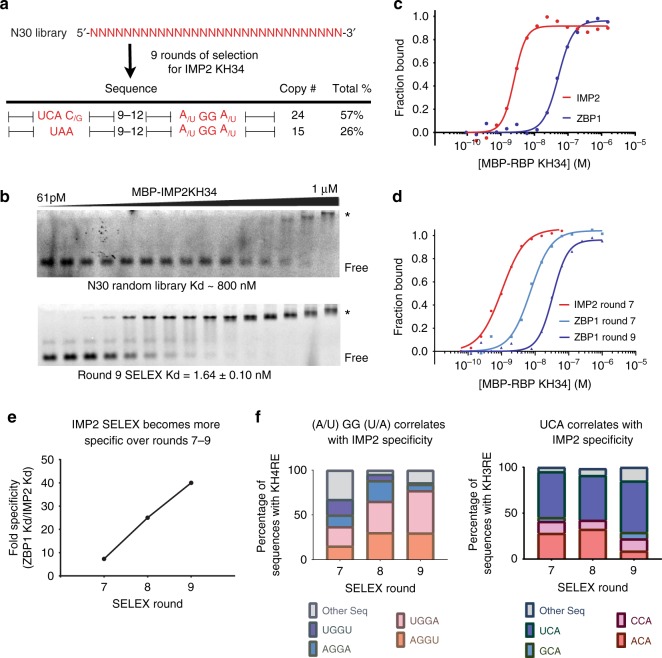
Fig. 2.
SELEX discovers targets that are IMP2 specific. a The sequences of RNAs after nine rounds of SELEX are shown. The range of nucleotide spacing between the nonrandomized IMP2 recognition elements is indicated for each sequence. Copy number and percentage of pool are listed. b Representative EMSAs for N30 SELEX library (top) and round 9 SELEX library (bottom). The filled triangle represents a 1:1 serial dilution of IMP2KH34. The RBP–RNA complex (*) and free RNA (FREE) are labeled. c Quantification and fit to the Hill equation of representative EMSA results for IMP2KH34 (solid red line) and ZBP1KH34 (solid blue line) binding to the round 9 SELEX library pool. d Quantification and fit to the Hill equation of representative EMSA results for IMP2KH34 (Round 7, solid red line) and ZBP1KH34 (round 7, solid cyan line, round 9, solid blue line) binding to different SELEX library pools. e Quantification of SELEX specificity for IMP2KH34 within each round SELEX library pool. The library specificity was calculated as the ratio between the Kd of ZBP1KH34 and the Kd of IMP2KH34 at a particular round of selection. f After sequencing each round of SELEX, the individual “GG” (left) and “CA” (right) motif occurrences were counted as a percentage of total SELEX sequences. The four most abundant motifs were plotted in terms of their relative abundance in each of the sequenced SELEX rounds. Source data are provided as a source data file