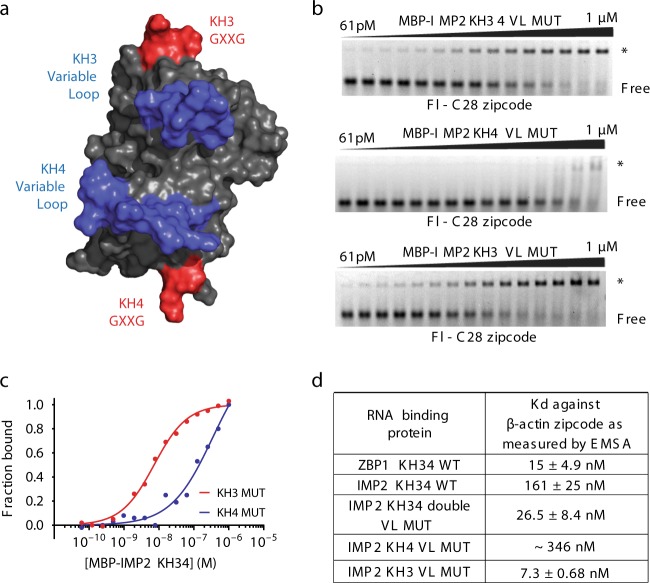
Fig. 4.
Mutations of the KH3 variable loop are sufficient to determine RNA-binding. a Surface rendering of IMP2KH34 shows putative binding site of RNA with variable loops in blue and GXXG motifs in red. b Top: double loop replacement allows for IMP2 to now bind to the ß-actin zipcode. Middle: the KH4 loop swap by itself does not increase affinity to the ß-actin zipcode compared to WT IMP2KH34. Bottom: KH3 variable loop replacement is sufficient to swap the specificity of IMP2KH34 and allow it to bind to ß-actin zipcode. c Quantification and fit to the Hill equation of top and middle representative EMSA results (in b) for IMP2KH3 VL MUT (solid red line) and IMP2KH4VL MUT (solid blue line) binding to ß-actin zipcode. d Dissociation constants (Kd) of ZBP1KH34 WT (gel in Fig. 1c), IMP2KH34 WT (gel in Fig. 1c), and the IMP2 variable loop mutants (i.e., KH34 double VL MUT, KH3 VL MUT, and KH4 VL MUT) and ß-actin zipcode measured by EMSA