Fig. 3.
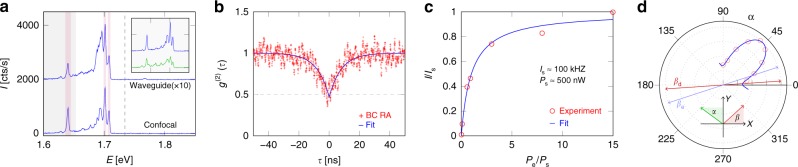
On-chip single photon emission. a Confocal and waveguide-coupled spectrum of spot S5, excited with λ = 702 nm. The waveguide spectrum is multiplied by 10 and offset by 2000 cts/sec for improved visualization. Common peaks are highlighted by the shaded purple regions. A 715 nm (1.73 eV) longpass filter, marked by the dashed line, was used to filter the pump. For the g(2)(τ) measurement a 750 nm (1.65 eV) longpass filter (gray shaded area) was used to isolate the single emitter at 756.6 nm (1.64 eV). The inset figure shows confocal spectra obtained by either green (λ = 532 nm) excitation (green curve) or excitation with λ = 702 nm (blue curve). b–d Characterization of the 1.64 eV emitter. b Normalized background-corrected (BC) running average (RA) coincidence counts (red) and g(2)(τ) fit (blue). c Measured intensity saturation (red) and fit to saturation curve (blue). d Normalized SPD count of the emitter (red) as a function of half-wave plate rotation angle α and fit to intensity transmission curve (blue); α = 0 corresponds to a half-wave plate fast axis along the Y−direction. See Supplementary Fig. 1 for orientation of the half-wave plate with respect to the (X, Y, Z) axes. Based on the fit, the difference in polarization angle between the PL (βd) and excitation (βe) beam can be extracted; β = 0 corresponds to a polarization along the X−axis