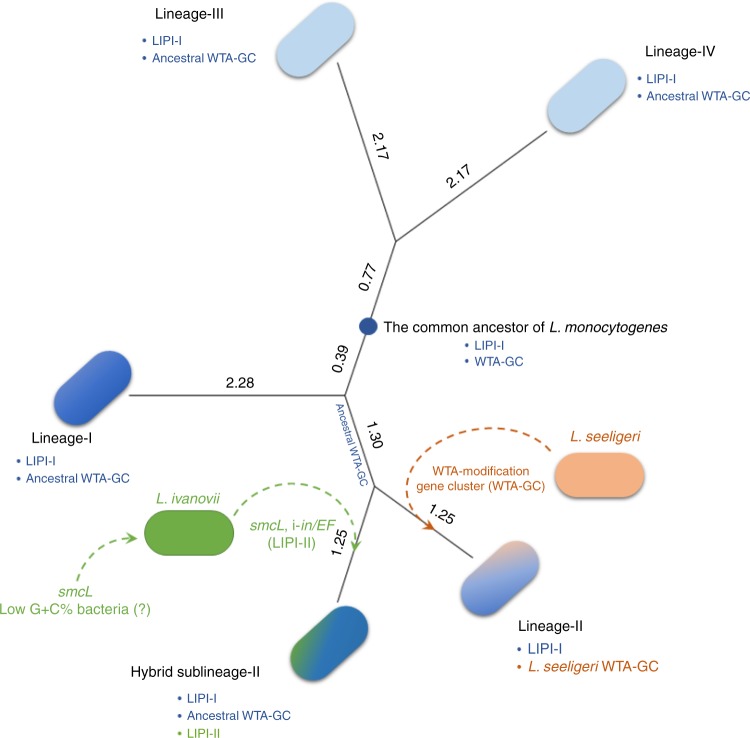
Fig. 8.
Evolutionary model of L. monocytogenes HSL-II. The phylogram is constructed using MUMmer-based average nucleotide identity (ANIm) of closed genomes of all lineages. The lineages are proposed to originate from a common ancestor possessing a 4b-like wall teichoic acid gene cluster (WTA-GC). For Lineage II, subsequent recombination events led to replacement of WTA-GC from L. seeligeri. Lineage II and HSL-II then separated and followed independent evolutionary paths. Ecological coexistence of HSL-II with other Lm lineages and L. ivanovii led to exchange and acquisition of genetic clusters, including a partial LIPI-II locus. The number next to each clade represents the %ANIm difference from respective last common ancestor. The topology of the tree is identical to the phylogenomic tree calculated based on the core genome (as in Fig. 2). WTA-GC: wall teichoic acid gene cluster