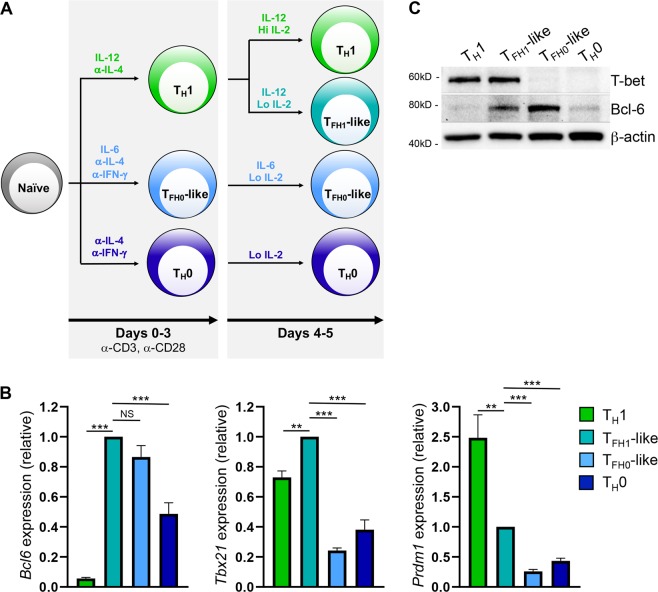
Figure 1.
TFH1-like cells derived from TH1 cells uniquely co-express Bcl-6 and T-bet. (A) Schematic depicting culturing conditions utilized for the differentiation of the indicated cell populations. Briefly, naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured on plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 as follows: TH1 (5 ng/mL IL-12, 5 μg/mL anti-IL-4), TFH0-like (50 ng/mL IL-6, 10 μg/mL anti-IL-4, 10 μg/mL anti-IFN-γ), or TH0 (10 μg/mL anti-IL-4, 10 μg/mL anti-IFN-γ). After 3 days, cells were removed from stimulation and plated under the following conditions: TH1 (5 ng/mL rmIL-12, 2.5 μg/mL anti-IL-4, 500 U/mL rhIL-2), TFH1-like (expanded from TH1 population; 5 ng/mL rmIL-12, 2.5 μg/mL anti-IL-4, 10 U/mL rhIL-2), TFH0-like (10 μg/mL anti-IL-4, 10 μg/mL anti-IFN-γ, 50 ng/mL rmIL-6, 10 U/mL rhIL-2), or TH0 (10 μg/mL anti-IL-4, 10 μg/mL anti-IFN-γ, 10 U/mL IL-2) for an additional 2 days. (B) qRT-PCR was used to assess expression of the indicated genes. The data were normalized to Rps18 and presented as fold change relative to the TFH1-like sample (mean of n = 4–7 ± s.e.m.). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple-comparison test. (C) Immunoblot analysis of Bcl-6 and T-bet protein expression in the indicated T helper cell populations. β-actin serves as a loading control. Shown is a representative blot of four independent experiments.