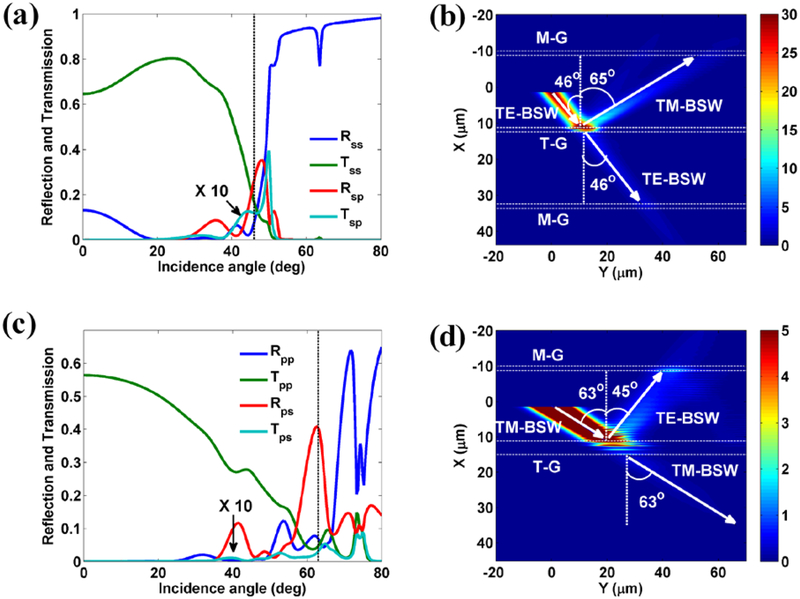
Figure 9. Modes transformation between TM-BSW and TE-BSW.
(a) The reflection, transmission and mode conversion efficiencies of TE-BSW propagating across two grooves versus the incidence angle. (b) The electric field intensity distribution for the BSW when the TE-BSW strikes to the transforming grooves (T-G) with incidence angle at 46° (denoted by vertical dashed line in (a)). (c) The reflection, transmission and mode conversion efficiencies of TM-BSW propagating across four grooves versus the incidence angle. (d) The electric field intensity distribution for the BSW when the TM-BSW strikes to the transforming grooves (T-G) with incidence angle at 63° (denoted by vertical dashed line in (c)). The white dashed lines parallel to the Y axis in (b) and (d) denote the exterior boundaries of the T-G and M-G. The mode conversion efficiencies of Tsp and Tps (shown in (a) and (c)) are magnified by a factor of 10. The structural parameters of all the grooves and dielectric multilayer are the same as those used in the experiments (Fig. 5), respectively.