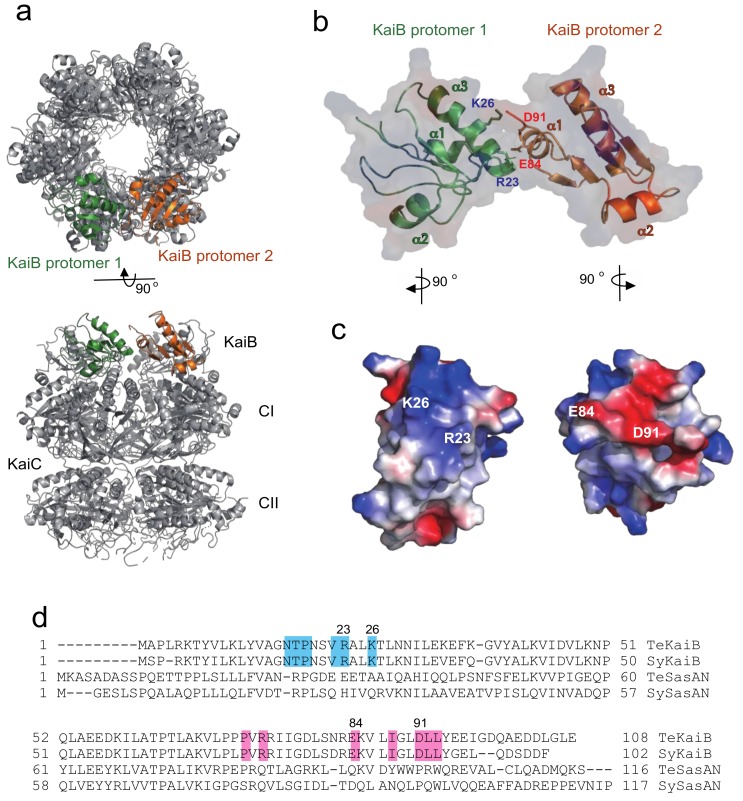
Figure 1.
KaiB–KaiB interface in the KaiB–KaiC complex. (a) Overall structure of the KaiB–KaiC complex. This structural model is based on the amino acid sequence of wild-type TeKaiB and the crystal structure of the complex in which TeKaiB has three mutation sites (PDB code: 5JWQ). The KaiC hexamer forms a double-ring structure composed of CI and CII rings and KaiB forms a hexameric ring on the CI ring. The two KaiB protomers are colored green and orange. (b,c) The KaiB–KaiB lateral interaction and surface electrostatic complementarity between two KaiB protomers. (d) Sequence alignment of KaiB and SasA originating from Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 and Thermosynechococcus elongatus. Sequences were aligned using the Dali server. The residues involved in the KaiB–KaiB lateral interactions are highlighted in cyan (protomer 1) and pink (protomer 2).