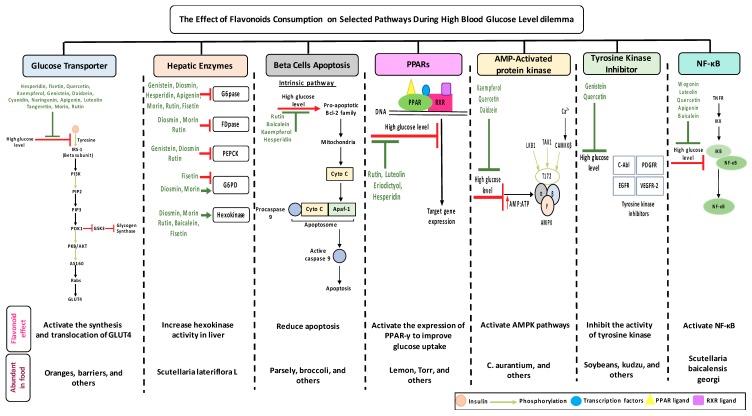
Figure 3.
Flavonoids as anti-diabetic agents: Modes of Action. Aberrant signaling pathways (Glucose transporter, hepatic enzymes, beta cell apoptosis, PPARS, AMPK, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and NF-κB) and pathway components targeted by flavonoids (highlighted in green). Flavonoids have a wide range of anti-diabetic actions where one flavonoid could target multiple pathways. These phytochemicals can enhance or suppress (green and red lines respectively) the activity of GLUT 4 translocation, glucose uptake by the tissue, and hepatic enzymes activities; causes a decrease in apoptosis and tyrosine kinase inhibition that improves the pathogenesis of diabetes (see text for detailed modes) of action for flavonoids mentioned). For abbreviation, see abbreviation list.