Table 3.
Representative flavones and their underlying anti-diabetic effects.
| Flavonoid Subclass | Name of Flavonoid | Structure of Flavonoid | Dietary Source | Metabolites Produced from Flavonoids | Function of Flavonoids | Mechanism of Action | Model Used | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In Vitro | ||||||||
| Flavones | 10. Baicalein |
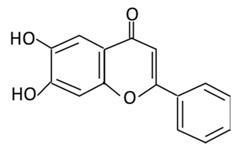
|
Scutellaria lateriflora L, and Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | In Intestine: Baicalin will be converted into Baicalein and then absorbed rapidly. In the circulation: Baicalein will be converted to Baicalin |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect |
Reduce the level of level of hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) Suppress the activation of NF-κB Improve glucose tolerance and insulin secretion from pancreatic cells Improve viability of clonal β-cells which improves the production of NADH and NADPH Protect against β cells apoptosis Increase hexokinase activity in liver Activate MAPKs signaling pathway which reduce the effect of insulin resistance by phosphorylating Akt and IRS-1 and dephosphorylate NF-κB Suppress fatty acid synthesis |
Obese diabetic mice Type 2 diabetic rats |
CA1 hippocampal neurons | [187,190] |
| 11. Luteolin |
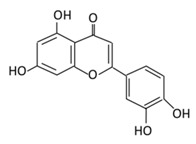
|
Parsley, broccoli, onoins leaves, celery, cabbages, apple skins, carrots, and peppers | Metabolization is medicated by UGTs and COMTs to produce: (A) Luteolin-7-glucuronide (Glucuronidated) (B) Luteolin-4-glucuronide (C) Chrysoeriol/diosmetic (Methylated) (D) Luteolin monoglucuronide (Major form in human serum |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect |
Reduce cAMP response element binding protein and histone acetyl transferase activity of CBP/p300 (NF-κB coactivator) Reduce apoptosis Up-regulate the espression of synaptic protein which target brain cells Improve insulin secretion by supressing Maf A through NF-κB signiling pathway Activate PPAR-γ which targets adiponectin, leptin and GLUT4 genes |
Obese mice Streptozotocin induced diabetic rats Diabetic rats |
Endothelium cells Human monocytes cells |
[155,157] | |
| 12. Diosmin |
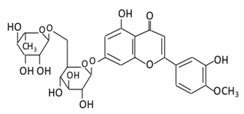
|
Citrus fruites, and Scrophularia nodosa L. | (A) Diosmin (Not excreted in urine) (B) Diosmetin (Not excreted in urine) (C) Minor metabolites in the form of glucuronic acid conjugate (Excreted in urine) |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect: |
Reduce the level of hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) due to increase in glutathione peroxidase (GPx) Decrease G6Pase, PEPCK, and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase enzymes Reduce plasma glucose and increase plasma insulin by activating anti-oxidant enzymes Reduce hyperglycemia by inducing β-endorphin Increase hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity Reduce lipid peroxidation |
Streptozotocin nicotinamide induced diabetic rats |
[179,180] | ||
| 13. Apigenin |
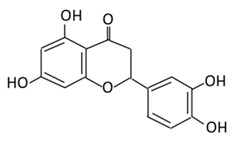
|
Onion, oranges, tea, parsley, chamomile, Hypericum perforatum L, wheat sprouts | Metabolization occurs through two phases: Phase (1): Apigenin produce three monohydroxylated: a) Luteolin b) Scutellarien c) iso-scutellarein Phase(2): Luteolin produce: a) Four monoglucuroconjugates b) Two Sulfoconjugate c) One methyl conjugate |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect: |
Reduce cellular antioxidants Attenuate cell damage in pancreatic β-cells Improve the morphology of the cells Improve GLUT4 translocation which lowers glucose level Increase serum cholesterol Increase lipid peroxidation |
Streptozotocin induced diabetic rats (0.2%) |
HepG2 cells Differentiated3T3-L1 cells |
[147,149] | |
| 14.Tangeretin |
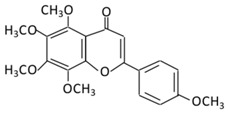
|
Poncirus trifoliate L, citrus fruit rinds, and mandarin orange | Metabolization is medicated by CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 to produce: (A) 4′ hydroxy - 5, 6, 7, 8 tetramethoxyflavone (4′-OH-TMF) |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect: |
Reduce blood glucose and HbA1c level Reduce the secretion of insulin resistance factor Increase the secretion level of insulin and insulin sensitizing factor Enhances glycolytic enzyme in the liver Reduce total cholesterol and adipocytokines level |
Rats Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats High fat diet mice |
Pancreatic β-cells | [160,162] | |
| 15. Wogonin |
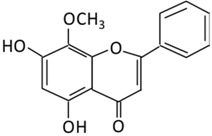
|
Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | (A) Wogonin-7-beta-D-glucuronide (Major metabolites) (B) Wogonin-5-beta-D-glucuronide |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect: |
Reduce hyperglycemia and lipid droplets accumulation in the liver Increase vascular permeability and the expression of cell adhesion molecules Activate NF-κB and AMPK pathways Activate PPARα which has a beneficial effect on lipid metabolism |
db/db mice | 3T3-L1 cells | [173,175] | |
| 16. Chrysin |
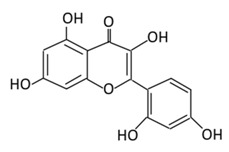
|
passiflora caerulea (L,), honey, Tilia tomentosa Moench, and Pelargonium crispum (Berg.) | (A) Chrysin glucuronides (M1) (B) Chrysin sulfates (M2) |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect: |
Reduce the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines that helps in the prevention of diabetic neuropathy Reduce blood glucose Improve renal pathology with the suppression of TGF-β, collagen-IV, and fibronectin Improve insulin level Reduce lipid peroxidation |
INS-1E cells | [167,169] | ||
