Table 4.
Representative isoflavones, anthocyanins and their underlying anti-diabetic effects.
| Flavonoid Subclass | Name of Flavonoid | Structure of Flavonoid | Dietary Source | Metabolites Produced from Flavonoids | Function of Flavonoids | Mechanism of Action | Model used | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In Vitro | ||||||||
| Isoflavones | 17. Genistein |
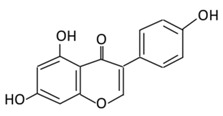
|
Soybeans, kudzu, and fava bean |
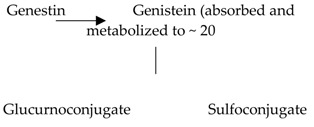
|
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect |
Reduce hyperglycemia through the activity of cAMP/ PKA pathway Decrease Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and p-ERK Inhibit the activity of tyrosine kinase Improve glucose intolerance and β-cells mass Decrease urinary excretion of TBARs |
Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats Obese diabetic mice Nongenetictype 2 diabetic mice |
INS-1 cells Human islet β-cells |
[195,199] |
| 18. Daidzein |
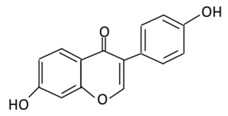
|
Soybeans, nuts, and soy milk | (A) Daidzin | (A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: | Decrease blood glucose, total cholesterol, and AMPK phosphorylation | Golden Syrian hamsters | [202,204] | ||
| Anthocyanins | 19. Cyanidin |
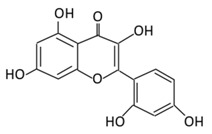
|
Bilberry, blueberry, grapes, blackberries, hawthorn, acai berry, and raspberry | (A) Anthocyanidin glucuronide conjugates (Major form in urine) (B) Simple Aglycones (Second major in urine) (C) Anthocyanidin methyl glucuronide conjugates (8 forms) (D) Cyanidin-3-glucoside E) Cyanidin-3-galactoside |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect: |
Inhibit α-glucosidase and α-amylase which reduce the absorption of glucose in small intestine Reduce fasting glucose level Prevent pancreatic apoptosis Improve antioxidant status which protects hepatocytes from HG-induced damage Attenuate aortic lipid peroxidation |
Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats db/db rats high fat diet fed mice |
Mouse hepatocyte | [207,209] |
| 20.Delphinidin |
|
Dark grapes, eggplant, berries, red cabbage, carrot, and tomato | (A) 4′-O- methyl delphinidin 3-O-beta-d- glucopyranoside | (A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: |
Reduce the glycation rate of HbA1c Prevents diabetes associated injuries such as endothelial cell function |
Diabetic mouse | [213,215] | ||
| 21.Pelargonidin |
|
Bilberry and ficus bengalensis Linn | (A) Pelargonidin-O-glucuronide (B) Pelargonidin-3-galactoside |
(A) Antihyperglycmeic effect: (B) Hypolipemic effect: |
Reduce hyperglycemia Reduce the level of antioxidant defensive enzymes Stimulate insulin secretion Reduce the level of TBARS which is a byproduct of lipid peroxidation |
Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats Diabetic rats |
[217,219] | ||
