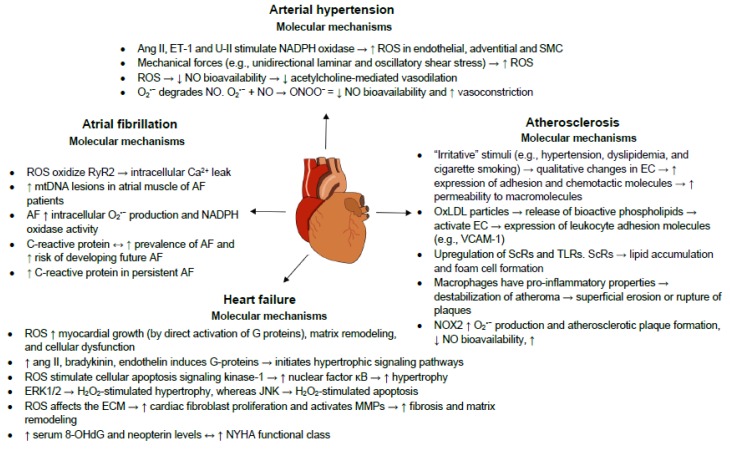
Figure 2.
Selected cardiovascular diseases and their underlying oxidative and inflammatory molecular mechanisms. 8-OHdG: 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine AF: atrial fibrillation; Ang II: angiotensin II; EC: endothelial cells; ECM: extracellular matrix; ERK 1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; ET-1: endothelin 1; H2O2: hydrogen peroxide; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NO: nitric oxide; NYHA: New York Heart Association; O2−: superoxide anion; ONOO−: peroxynitrite; OxLDL: oxidatively modified LDL; ROS: reactive oxygen species; RyR2: type 2 ryanodine receptor; ScRs: scavenger receptors; SMC: smooth muscle cells; TLRs: toll-like receptors; U-II: urotensin II; VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; →: leads to; ↔: associated with. Please refer to the text for more details.